As of 2024, there are nearly 19 billion connected IoT devices worldwide, and this number is expected to continue growing (IoT Analytics). However, without right strategies to manage connectivity, interoperability, and data integration, businesses risk missing out on the full potential of IoT.
Manufacturers today rely heavily on IoT. Devices like sensors, machines, and wearables generate massive volumes of data. Yet, most devices work in silos. This creates a significant challenge of slow and fragmented decision-making.
Traditional IoT development alone cannot solve these problems. Organizations need Inter IoT strategies that enable devices, platforms, and applications to work together seamlessly. The advanced connectivity technology ensures smooth data flow with a reliable IoT connection across multiple devices.
Here, we will explore practical Inter IoT strategies that simplify IoT management, enhance connectivity, and empower enterprises to make smarter decisions every day.
Let’s understand!
What is Interoperability in IoT?
Interoperability in IoT is the ability of devices, systems, and platforms to communicate, share data, and work together seamlessly. Ensuring interoperability is crucial for developing smart applications and services. Particularly as the number of IoT devices increases exponentially, generating huge volumes of heterogeneous data.
Definition:
Interoperability in IoT refers to the ability of heterogeneous IoT devices, systems, and software platforms to exchange data and execute coordinated operations seamlessly, regardless of differences in manufacturer, communication protocols, hardware architecture, or data formats.
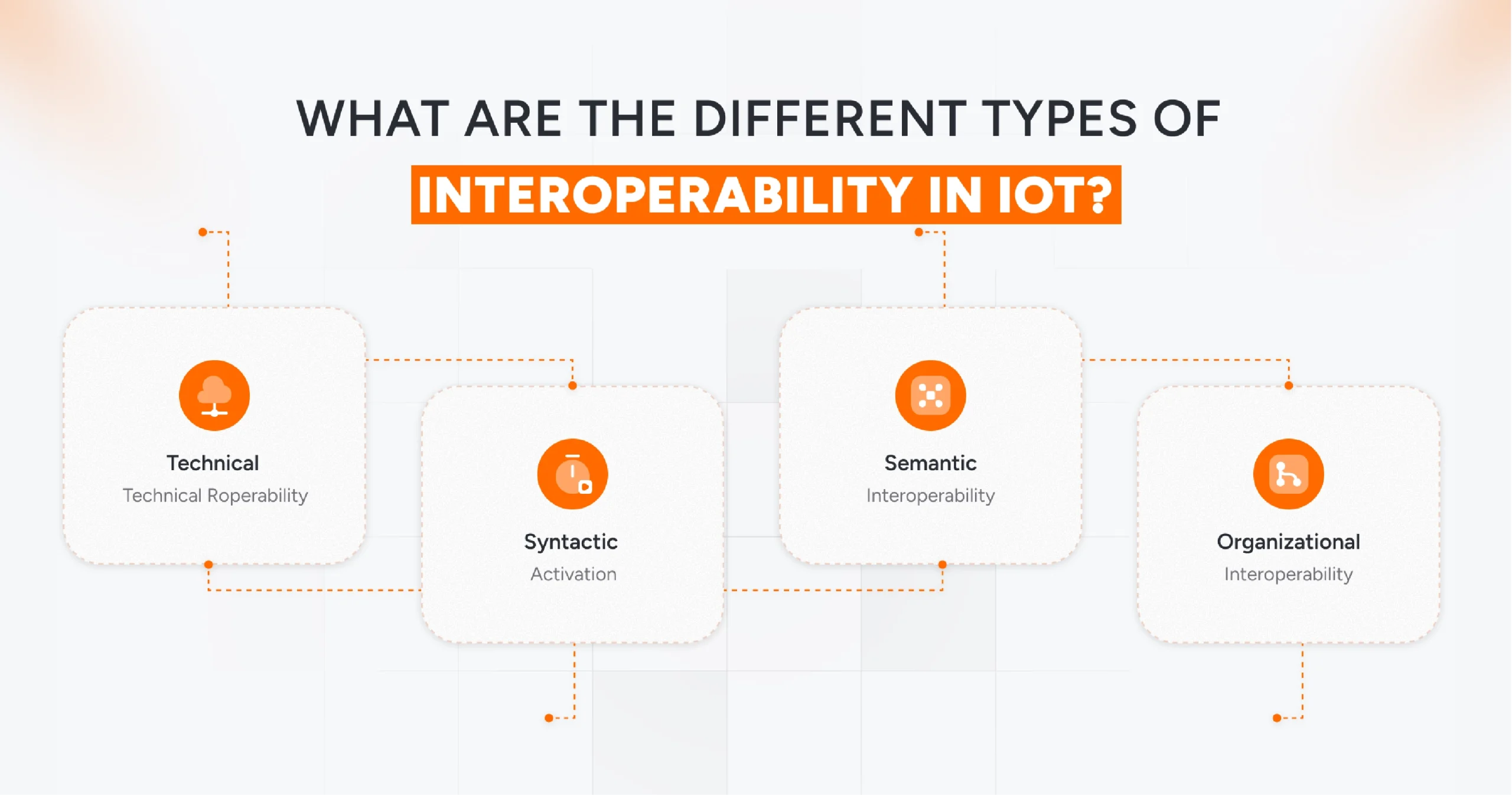
What are the Different Types of Interoperability in IoT?
Interoperability is not a one-dimensional concept. It operates across multiple layers of IoT ecosystems. Understanding them from expert manufacturing IT services & solution providers can help streamline these connections. They make it easier to manage diverse devices, legacy equipment, and modern platforms without disruption.
Let’s examine how each type contributes to ensuring seamless collaboration among devices, platforms, and enterprise systems.
InteTechnical roperability
This is the foundation of IoT interoperability. It ensures that devices can actually connect and share data over a network. Without it, IoT devices remain siloed. The basic thing it does is,
- Involves hardware, connectivity technology, and communication protocols.
- Ensures smooth data exchange across Wi-Fi, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Zigbee, LoRaWAN, or NB-IoT.
- Ensures that IoT sensors, gateways, and cloud systems can communicate with each other reliably and securely.
This brings significant relief to manufacturers. It reduces integration headaches by ensuring a unified IoT architecture across devices from different vendors.
Syntactic interoperability
Once devices connect, the next hurdle is how they format and share data. This is where syntactic interoperability plays its role.
- Focuses on data formats and structures (e.g., JSON, XML, CBOR).
- Enables IoT software platforms to parse, validate, and process incoming data without errors.
- Helps avoid costly inconsistencies that slow down IoT product development.
Imagine one device sending “25” as a temperature value in Celsius, while another sends “77” in Fahrenheit. Without syntactic rules, the system might misread or misapply data, impacting decision-making.
Semantic Interoperability
Syntactic consistency isn’t enough if the meaning of the data isn’t shared. Semantic interoperability ensures that IoT data is understood uniformly across platforms and applications.
- Uses ontologies, metadata, and shared vocabularies to define meaning.
- Ensures a “temperature reading” from one IoT device has the same context everywhere in the ecosystem.
- Critical for advanced use cases like predictive maintenance, healthcare IoT, or industrial automation.
This is where enterprises unlock actionable insights. It precisely turns raw IoT data into intelligence that drives smarter manufacturing analytics strategies.
Organizational Interoperability
The top layer of IoT interoperability goes beyond devices. It’s about aligning business processes and enterprise systems to effectively act on IoT insights.
- Ensures IoT data flows into ERP, CRM, or analytics platforms.
- Supports IoT strategies that enhance workflows, minimize downtime, and improve the customer experience.
- Requires collaboration between IT, operations, and business teams for maximum impact.
Without this layer, even the best IoT architecture remains underutilized. With it, enterprises gain end-to-end value from IoT investments.
What are the Key Challenges in IoT Interoperability for Manufacturers?
This brings significant relief to manufacturers. It reduces integration headaches by ensuring a unified IoT architecture across devices from different vendors. One of the biggest hurdles is interoperability.
Even with the right IoT development strategy, enterprises often hit barriers that slow adoption and limit ROI. Let’s break down the main challenges:
1. Diverse Device Ecosystems
IoT ecosystems rarely come from a single vendor. Instead, they’re composed of sensors, gateways, and applications developed by multiple manufacturers. Each comes with its own standards and compatibility requirements.
- A smart factory may have machines from ten different vendors.
- A healthcare setup might use monitoring devices that don’t “speak” the same language.
Without interoperability, devices remain locked in silos, preventing enterprises from seeing the full picture.
2. Multiple Communication Protocols
IoT thrives on connectivity, but here’s the problem: there are too many protocols.
- Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), LoRaWAN, and NB-IoT are common technologies, but they are not always compatible with each other.
- Some are designed for low power and long range, while others focus on high data throughput.
When different parts of the IoT architecture utilize various communication technologies, enterprises often require complex middleware or custom integrations, which increases costs and delays deployment.
3. Data Inconsistencies
Even if devices manage to connect, their data formats often don’t align.
- One device might log time in GMT, while another uses local time zones.
- Temperature could be measured in Celsius by one sensor, and Fahrenheit by another.
- File structures may vary, such as JSON, XML, or proprietary formats.
Without syntactic and semantic interoperability, this inconsistency creates data chaos, making it difficult to analyze trends or build reliable IoT strategies.
4. Security and Compliance Risks
Interoperability often means connecting more devices and systems, which expands the attack surface.
- Devices built without strong encryption standards become weak links.
- Sharing data across platforms raises concerns about data privacy, GDPR, and HIPAA compliance.
- Enterprises struggle to balance seamless IoT connect with strict regulatory needs.
Without careful planning, interoperability can unintentionally expose sensitive business or customer data.
5. Operational Misalignment
Even if the technology works, enterprises often face a people and process challenge.
- Teams may not be trained to interpret IoT insights.
- Data might not flow into ERP, CRM, or analytics systems in a usable way.
- Departments may disagree on who owns IoT data and how it should be used.
This misalignment often leads to underutilization of IoT product development efforts, where valuable insights are collected but never acted upon.
All these challenges require a holistic IoT strategy, supported by robust IoT product development and engineering solutions that understand both technological and business needs.
IoT Architecture & Connectivity Technology
Every successful IoT solution stands on two pillars: a strong architecture and reliable connectivity technology. For manufacturers, these are not just technical choices—they directly impact production efficiency, scalability, and the ability to make smarter decisions at every level of the business.
Breaking Down IoT Architecture
At its core, IoT architecture serves as the blueprint that illustrates how devices, data, and applications interact and work together. Think of it as the nervous system of your manufacturing operations. It includes sensors on the shop floor to analytics dashboards in the boardroom.
A typical IoT architecture includes:
- Perception Layer (Sensors & Devices): Machines, equipment, and environmental sensors that collect real-time data.
- Network Layer (Connectivity): Technologies such as Wi-Fi, LoRaWAN, Zigbee, or NB-IoT are used to transmit this data securely.
- Edge Layer (Gateways & Edge Computing): Devices that process data closer to where it’s generated, reducing latency and improving real-time responses.
- Data Management & Processing Layer (Cloud/On-Prem Systems): Platforms where raw data is stored, filtered, and analyzed for trends and patterns.
- Application Layer (Business Insights): Dashboards, predictive analytics, and ERP/CRM integrations where decision-makers see actionable intelligence.
IoT architecture ensures scalability, security, and interoperability. For manufacturers, it translates to fewer disruptions, better visibility, and data-driven decision-making.
The Role of Connectivity Technology
Without reliable connectivity, IoT is just a set of disconnected devices. Connectivity technology is what enables “things” in the Internet of Things to communicate with each other.
Some of the most common connectivity options for manufacturing IoT include:
- Wi-Fi: High bandwidth, suitable for indoor environments like factories.
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE): Great for short-range, low-power needs such as equipment tracking.
- Zigbee & Z-Wave: Often used in industrial automation for low-power mesh networking.
- LoRaWAN: Ideal for long-range, low-power use cases like remote monitoring.
- NB-IoT / LTE-M: Cellular technologies designed for massive IoT deployments with reliable coverage.
- 5G: The emerging powerhouse offering ultra-low latency, real-time data streaming, and scalability for advanced manufacturing.
For manufacturing leaders, the choice of connectivity determines:
- How quickly machines communicate.
- How secure and reliable is the data flow?.
- How well the IoT solution can scale across facilities and geographies.
- Why This Matters to Manufacturing Enterprises
Basically, IoT architecture defines how seamlessly systems integrate with existing IT, ERP, or MES systems. Connectivity choices impact latency, bandwidth, and interoperability.
It’s about outcomes. Reduced downtime, predictive maintenance, and operational visibility. The right architecture and connectivity mean better margins, smarter investments, and a competitive advantage.
IoT architecture and connectivity tech aren’t background concerns. They’re the backbone of IoT in the manufacturing space. When they’re done right, they turn factories into smart, connected ecosystems where real-time insights guide every decision and keep operations moving with intent.
How IoT Product and Software Development Works
Building an IoT solution is never just about connecting devices. It is about creating an ecosystem that works reliably, securely, and at scale. The development process needs structure, foresight, and constant iteration.
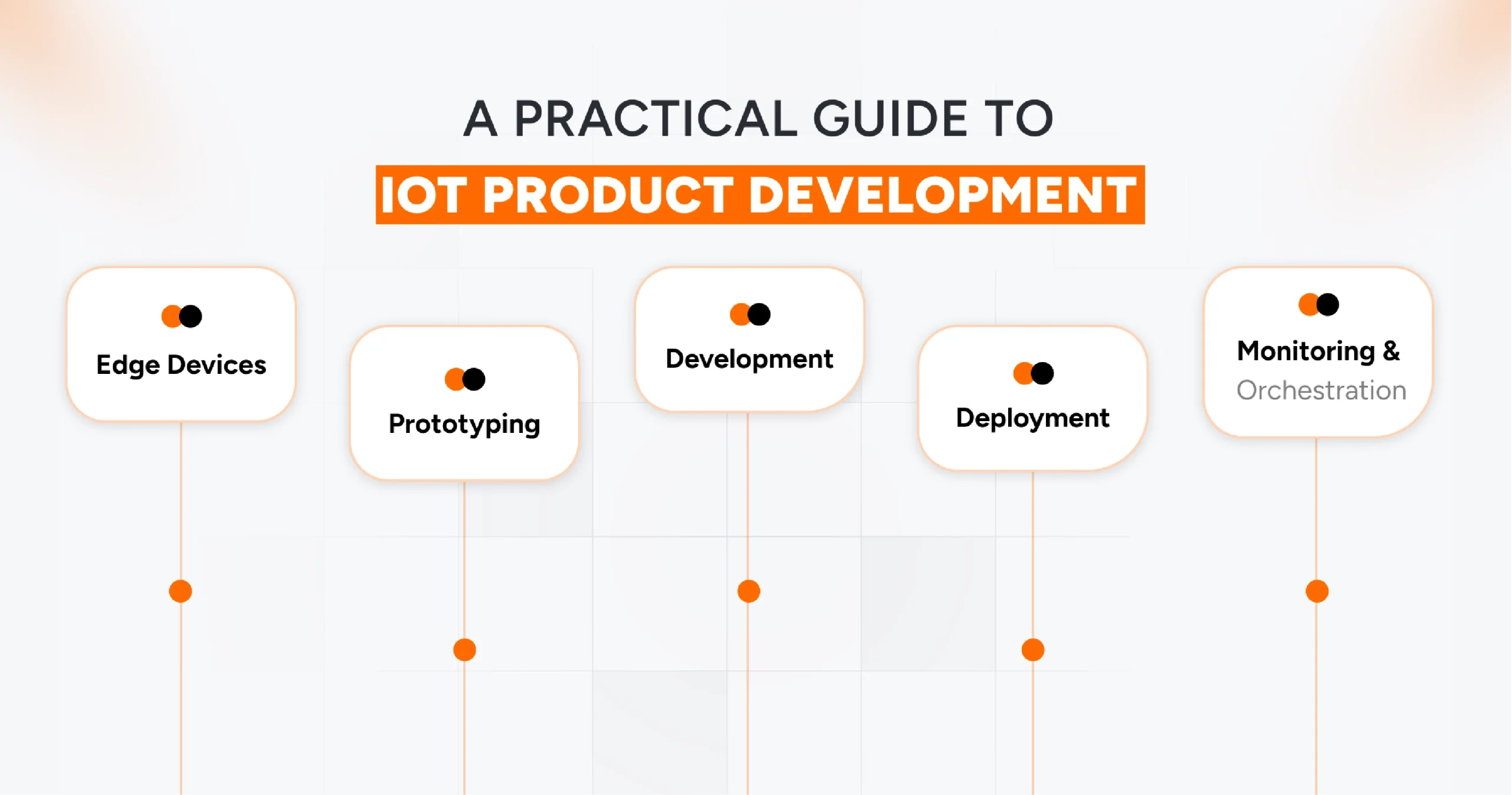
A Practical Guide to IoT Product Development
IoT product development follows a lifecycle that ensures every stage is addressed. From idea to deployment, every step adds measurable value.
- Concept – Everything starts with clarity. The product vision must align with business goals, identify practical use cases, and define how IoT adds efficiency or intelligence. A strong concept helps set the right technical and strategic direction.
- Prototyping – Before investing heavily, proof-of-concept models are built. These prototypes validate hardware compatibility, test connectivity technologies (Wi-Fi, LPWAN, 5G, and Bluetooth), and simulate data flow to ensure seamless operation. It’s where assumptions are challenged and risks reduced.
- Development – This is where the foundation becomes real. Firmware is written for devices, cloud platforms are integrated, APIs are built, and user applications are designed. Interoperability remains the core focus, enabling devices to communicate seamlessly within larger IoT architectures.
- Deployment – Rolling out an IoT product is more than switching it on. It requires system-wide integration, performance testing under real conditions, and setting up monitoring frameworks to ensure reliability as the ecosystem scales.
- Monitoring & Optimization – The lifecycle doesn’t end after launch. Devices must be updated, security patches applied, and data monitored for insights. Continuous optimization ensures IoT products stay resilient, scalable, and future-proof.
This structured approach not only avoids costly missteps but also accelerates time-to-market while ensuring long-term reliability.
Why Device Management Matters in IoT?
Device management isn’t a background task. It’s the backbone of IoT success. It ensures every connected device:
- Performs consistently across environments
- Stays secure with updates and patches
- Scales as more devices join the network
- Delivers accurate data for informed decisions
Without robust device management, even the most advanced IoT product risks downtime, vulnerabilities, and inefficiencies.
5 Best Practices in IoT Software Development
Developing IoT software is about more than writing code. It is about building systems that are reliable, secure, and scalable, enabling devices to deliver real business value.
Following the right approach at every stage ensures IoT initiatives succeed.
1. Secure IoT from Day One
Security is built in from the beginning. Devices and systems are designed to ensure safe operations and protect data.
- Strong encryption, like TLS and AES, secures communication.
- Access controls and authentication protect users and administrators.
- Compliance with standards such as ISO/IEC 27001 and GDPR ensures the safe handling of data.
This approach keeps systems resilient against cyber threats while allowing growth.
2. Seamless IoT Interoperability
Devices and platforms need to work seamlessly together.
- Open standards, such as MQTT, CoAP, and OPC UA, enable smooth communication.
- Flexible APIs connect IoT data to analytics tools and enterprise systems.
- Middleware bridges older systems with new technology when needed.
Focusing on interoperability ensures that IoT ecosystems remain flexible, adaptable, and easily scalable.
3. Future-Ready IoT Architectures
- IoT systems must grow without losing performance.
- Cloud-based infrastructure supports a greater number of devices and higher data volumes.
- Edge computing processes data close to the source, improving response times.
Microservices enable individual components of the system to scale independently, ensuring smooth operations. With scalable architecture design, IoT solutions remain efficient as networks expand.
4. Real-Time Insights for Better Results
Data is continuously used to improve devices and operations.
- Analytics identify issues, predict failures, and optimize processes to enhance efficiency.
- AI and machine learning enhance device intelligence over time.
- Feedback loops adjust device behavior to improve outcomes.
These data-driven feedback loops ensure IoT solutions turn information into actionable insights that drive results.
5. Continuous Integration and Deployment
- IoT systems are built to evolve continuously.
- Automated testing ensures updates maintain stability.
- Over-the-air updates keep devices current without interrupting operations.
Rapid deployment cycles enable the quick rollout of new features and fixes. This approach ensures that IoT solutions remain reliable, flexible, and future-ready.
Key Business Benefits of IoT & Inter IoT
The real value of IoT and Inter IoT solutions lies not just in connecting devices, but in transforming the way businesses operate and make decisions. When devices, systems, and software work together seamlessly, enterprises can unlock measurable advantages across multiple areas.
1. Improved Decision-Making
IoT turns raw data into actionable insights. Connected devices continuously collect and transmit information, allowing teams to make informed decisions quickly.
- Real-time analytics highlight trends and anomalies as they happen.
- Predictive insights enable the anticipation of future needs and challenges.
- Decisions are based on accurate, up-to-date data, reducing guesswork and errors.
2. Operational Efficiency
By connecting systems and streamlining workflows, IoT enhances efficiency across operations.
- Automation of repetitive tasks frees up human resources for higher-value work.
- Equipment monitoring ensures machines run at optimal capacity, reducing downtime.
- Interconnected processes allow faster responses to production changes or disruptions.
3. Cost Optimization
IoT enables smarter resource management, lowering operational costs without sacrificing performance.
- Energy usage can be monitored and optimized across facilities.
- Maintenance becomes predictive rather than reactive, avoiding costly breakdowns.
- Inventory and supply chain management become more precise, resulting in reduced waste and overstocking.
4. Predictive Insights
Interconnected IoT systems go beyond reporting what has already happened—they anticipate what might happen next.
- Advanced analytics identify patterns that indicate potential failures or opportunities for improvement.
- Predictive maintenance reduces unexpected downtime and extends the life of equipment.
- Forecasting production or demand helps plan resources more effectively.
AQe Digital and Connected IoT Systems
IoT becomes truly valuable when it solves real operational challenges and delivers actionable insights. AQe Digital focuses not just on connecting devices but on building systems that integrate seamlessly, adapt quickly, and generate measurable outcomes for manufacturing enterprises.
One of the key approaches is designing IoT solutions for cross-factory visibility. This enables teams to monitor operations across multiple locations without compromising control over day-to-day processes. Important elements include:
- Centralized dashboards to track equipment performance and production metrics.
- Data aggregation to spot inefficiencies early.
- Real-time insights that support quick decision-making.
- Adopting open standards to create a common language between devices.
- Flexible APIs that allow integration with enterprise systems.
- Bridging old and new technologies through middleware for seamless operations.
This combination of strategic architecture, interoperability solutions, and customized product development ensures IoT is more than a technical implementation—it becomes a practical tool for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and supporting smarter decision-making.
In a Nutshell
IoT and Inter IoT are transforming manufacturing by connecting devices, systems, and processes to deliver actionable insights. With the right approach, enterprises can enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and make smarter, data-driven decisions.
Your business can harness success from strategic IoT architecture, seamless interoperability, and tailored product development. These elements ensure that your connected systems are secure, scalable, and aligned with business goals, providing real operational and strategic value.
AQe Digital supports businesses in harnessing IoT effectively, designing solutions that address real-world manufacturing challenges. Connect with us to discover how your enterprise can leverage connected systems in your industry.
FAQs
We offer solutions that connect devices, software, and systems across your factory. From monitoring equipment to analyzing data in real time, our approach helps you see the bigger picture and make smarter decisions.
By linking machines, sensors, and platforms, you get insights into production trends, maintenance needs, and workflow bottlenecks. This enables your team to act more quickly and maintain smooth operations.
Absolutely. We handle interoperability challenges by using open protocols, flexible APIs, and bridging solutions so legacy equipment can connect seamlessly with modern systems without disruption.
Think of it as a full journey: concept → prototype → development → deployment → monitoring. At every stage, we focus on creating solutions that are practical, secure, and built to grow with your operations.
Yes. By analyzing equipment data and predicting maintenance needs, IoT can reduce downtime, optimize energy use, and minimize material waste, turning insights into measurable savings.
It depends on your setup and scale. We focus on phased deployment, so you start seeing benefits early, while the system continues to adapt and expand over time.