By 2025, the Internet of Things (IoT) is expected to power over 40 billion connected devices worldwide. These devices generate nearly 80 zettabytes of data annually. And yet, most organizations still rely on cloud-only processing, resulting in latency, bandwidth strain, and higher costs.
Especially in manufacturing, these delays can result in costly unplanned downtime, while in healthcare, they can compromise life-critical patient monitoring. For autonomous vehicles, even a single millisecond of lag can affect safety decisions. This is where edge computing can help, processing data at or near its source for real-time analytics, stronger security, and greater efficiency.
By combining IoT with edge computing, businesses can achieve faster responses, higher reliability, and the competitive agility necessary to thrive in today’s digital landscape. This article explores how it works, why it’s critical now, and where it’s headed.
What Makes IoT and Edge Computing a Powerful Combination?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is about connecting physical objects to the digital world. From wearables and smart homes to industrial machines and self-driving cars, these devices constantly generate, send, and analyze streams of data.
The magic happens when this data fuels real-time decisions, whether through human input or advanced AI and machine learning models. This is where the accurate intelligence of IoT emerges, turning simple connectivity into actionable insights.
Edge Computing: Redefining How IoT Operates
Now, here’s where edge computing shifts the game. Instead of relying solely on faraway data centers, it moves computation closer to the devices themselves.
Organizations that invest in IoT Product Engineering can leverage this approach to design smarter, more scalable, and highly responsive IoT systems. The result is:
- Lower latency
- Faster response times
- A smoother experience for both users and businesses
But for organizations, this isn’t just about speed. Edge computing also focuses on scaling resources efficiently across thousands of devices while maintaining reliable and consistent services.
The Future: 5G, Edge, and Intelligence at the Core
With 5G IoT edge computing, data doesn’t just move quickly; it moves at lightning speed, enabling advanced applications such as AR/VR, autonomous vehicles, and Data and AI/ML-powered solutions for fleet management that optimize operations in real-time.
It’s this powerful blend of connectivity, intelligence, and proximity that makes IoT and edge computing the perfect duo, shaping the next wave of digital transformation.
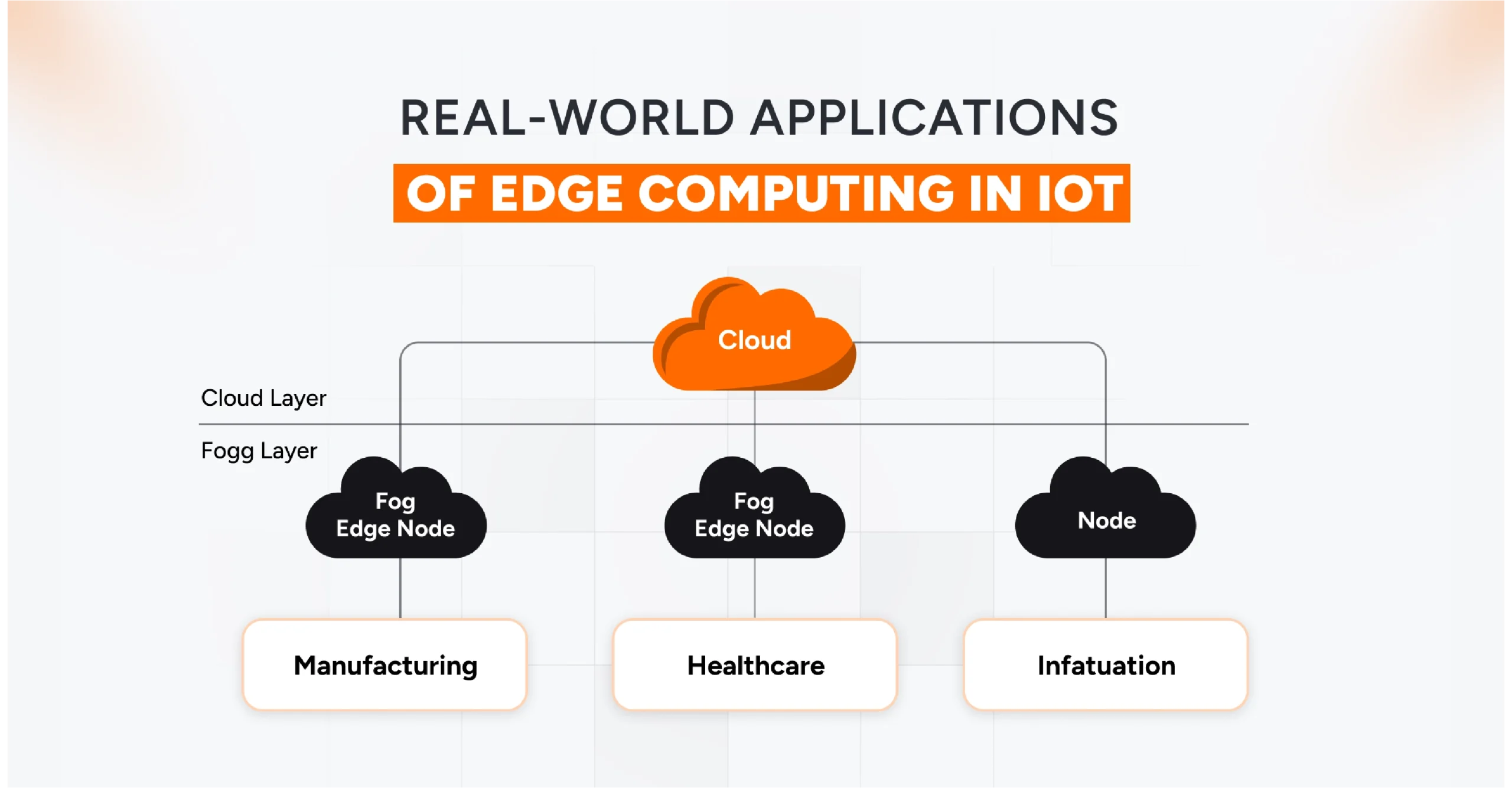
The Role of Edge Computing in IoT
Integrating IoT ensures speed and reliability. Whether it’s a smart factory floor, a self-driving car, or a connected hospital, every second counts; that’s why Edge Computing in IoT has quickly moved from buzzword to backbone. By processing data right where it’s created, edge computing cuts through latency, minimizes downtime, and unlocks use cases that the cloud alone could never handle.
Why Edge Computing Matters for IoT?
Traditional IoT setups leaned heavily on the cloud. But when you’re dealing with massive datasets or mission-critical tasks, waiting for distant servers to crunch numbers isn’t realistic. Edge computing solves this by:
- Delivering near-zero latency for time-sensitive actions.
- Reducing dependence on connectivity is a lifesaver in remote or bandwidth-limited environments.
- Boosting security and privacy by keeping sensitive data closer to its source.
- Ensuring resilience, since distributed systems don’t collapse if one node fails.
Edge computing doesn’t just make IoT faster. Industries such as automotive, healthcare, and manufacturing are leveraging edge solutions to enhance safety, reduce downtime, and optimize performance.
1. Manufacturing: Predictive Maintenance and Intelligent Automation
Edge computing plays a key role in predictive maintenance and production optimization. Connected sensors embedded within machines continuously capture telemetry data, including temperature, vibration, torque, and pressure.
Instead of sending this raw data to the cloud, IoT in the manufacturing ecosystem enables edge nodes to process it locally using AI/ML algorithms to detect anomalies or wear patterns in real time. When irregularities are identified, the system can automatically alert operators, trigger automated maintenance workflows, or even shut down equipment to prevent damage.
Technical Advantage:
- Reduced latency: Processing occurs near the machine, enabling responses within milliseconds.
- Bandwidth efficiency: Only processed or aggregated insights are sent to the cloud for long-term analytics.
- Integration potential: Seamless communication with IoT Product Engineering platforms and Data Analytics Systems ensures scalability and cross-factory intelligence.
2. Healthcare: Real-Time Patient Monitoring and Diagnostics
In healthcare, edge computing enables low-latency data processing for life-critical applications. Medical IoT devices such as ECG monitors, infusion pumps, or wearable biosensors generate a constant stream of patient vitals.
Through edge processing, this data is analyzed locally at hospital gateways or even on-device, allowing clinicians to make instant diagnostic decisions without relying on distant cloud servers. This is crucial in emergency care, remote patient monitoring, and telemedicine scenarios where real-time response can save lives.
Technical Advantage:
- Local AI inference: Edge devices use lightweight machine learning models for early detection of abnormalities (e.g., arrhythmia, oxygen desaturation).
- Data security and compliance: Patient data remains within the hospital network, ensuring adherence to HIPAA and security and compliance standards.
- Operational continuity: Medical systems remain functional even if network connectivity fluctuates.
3. Critical Infrastructure: Edge-Based Security and Operational Resilience
For sectors such as energy, utilities, transportation, and smart cities, edge computing combined with cutting-edge smart devices enhances system resilience and security. Distributed sensors and controllers continuously monitor grid stability, water flow, or traffic patterns in real-time.
By processing data locally, edge systems enable instant fault detection, predictive load balancing, and intrusion prevention, even in the absence of stable cloud connectivity. They also enhance data integrity by isolating local systems from external threats while maintaining encrypted communication with centralized control rooms.
Technical Advantage:
- Real-time control: Local nodes execute decisions (e.g., rerouting power, closing valves) within milliseconds.
- Cybersecurity: Integrated Secure SaaS Solutions provide endpoint encryption, anomaly detection, and identity management.
- Resilient architecture: Systems continue functioning during cloud outages or network failures, ensuring operational continuity.
Difference Between IoT Device and Edge Device
Benefits Of Edge Computing in IoT
Here are some of the top benefits of using edge computing in IoT
Real-Time Latency Reduction
In IoT, milliseconds can make the difference between smooth operations and costly delays. Traditional cloud systems often introduce lag because data must travel long distances before decisions are made.
Edge Computing in IoT addresses this by processing data close to where it’s generated. This ensures faster responses, more reliable performance, and the ability to handle critical tasks in real time without waiting for cloud feedback.
How Does It Help Businesses In The Real World?
-> React to critical events instantly, avoiding delays in operations.
-> Make instant decisions using real-time insights from connected devices.
-> Perform computations locally (e.g., filtering, aggregating, running AI models)
The Impact:
Real-time processing enables businesses to transition from a reactive to a proactive approach, reduces operational downtime, and facilitates more agile decision-making.
Optimizing Bandwidth Usage
IoT devices generate large volumes of data, but not all of it needs to be transmitted to the cloud. Sending everything creates network congestion and increases costs.
Edge computing addresses this by filtering and analyzing data locally, sending only the relevant information to central systems. This approach reduces bandwidth usage, improves efficiency, and allows businesses to scale IoT operations without overloading their networks.
How Does It Help Businesses In The Real World?
-> Reduce unnecessary data transmission to save network resources.
-> Prioritize the most critical insights for faster decision-making.
-> Scale connected systems efficiently without overwhelming infrastructure.
The Impact:
Optimizing bandwidth ensures systems remain efficient, cost-effective, and scalable, thereby supporting long-term growth and performance in IoT environments.
Enhancing IoT Security
Each new connected device introduces potential security risks, and transmitting data over networks can create privacy and compliance challenges. Edge computing improves security by keeping sensitive data closer to its origin.
Local processing and storage enable businesses to control access, reduce exposure to cyber threats, and maintain privacy, without relying solely on remote servers.
How Does It Help Businesses In The Real World?
-> Maintain control over who can access critical data.
-> Reduce risk of data breaches by keeping sensitive information local.
-> Ensure privacy and compliance without compromising system performance.
The Impact:
With IoT and edge computing, businesses can confidently deploy connected systems knowing their data is more secure, operations are resilient, and trust with clients or users is reinforced.
Real-Time Data Analysis
Edge computing software eliminates processing delays, allowing organizations to receive actionable insights instantly. Decisions that previously required waiting for cloud analysis can now be made in real-time.
This supports faster problem-solving, improves operational efficiency, and enables organizations to capitalize on fleeting opportunities. By analyzing data at the edge, companies can respond immediately to changing conditions, trends, or anomalies without disrupting workflows.
How Does It Help Businesses In The Real World?
-> Identify and act on critical data patterns instantly.
-> Quickly resolve operational issues before they escalate.
-> Leverage fleeting opportunities that require fast reaction times.
The Impact:
Real-time data analysis enhances agility, responsiveness, and efficiency, resulting in faster and more competitive operations.
Remote Management
Edge computing platforms often come with centralized remote management tools, allowing organizations to monitor and control devices from anywhere. This capability simplifies operations, streamlines maintenance, and ensures that notifications, updates, and insights are always accessible via desktop or mobile devices.
Centralized control reduces the risk of downtime, simplifies troubleshooting, and ensures a consistent operational experience across distributed networks.
How Does It Help Businesses In The Real World?
-> Oversee and troubleshoot devices remotely.
-> Receive real-time alerts and operational insights.
-> Simplify device management across multiple locations.
The Impact:
Remote management improves operational visibility, reduces on-site intervention costs, and enhances overall system reliability.
Scalability
Edge computing enables businesses to expand device deployments and add functionality easily. Systems can handle increasing volumes of data without performance degradation, supporting growth in connected device networks.
This scalability ensures that organizations can adapt to evolving business needs, increasing capacity as demand rises or integrating new processes without requiring infrastructure overhauls.
How Does It Help Businesses In The Real World?
-> Add new devices seamlessly as operations grow.
-> Handle higher data volumes without impacting performance.
-> Introduce new functionality without complex reconfiguration.
The Impact:
Scalability enables businesses to efficiently grow their IoT ecosystem while maintaining performance, preparing them for future technological needs.
Cost Efficiency
Edge computing reduces the need for extensive cloud infrastructure and long-distance data transfers, enabling organizations to lower their operational costs. Localized processing and storage are often more cost-effective, particularly in resource-constrained environments.
By minimizing cloud dependency and optimizing bandwidth utilization, edge computing enables organizations to strike a balance between performance and budget considerations.
How Does It Help Businesses In The Real World?
-> Minimize cloud storage and processing expenses.
-> Avoid network overload and related costs.
-> Deploy cost-efficient infrastructure to support the expansion of IoT systems.
The Impact:
Cost containment allows businesses to implement scalable IoT systems without overspending, making technology adoption more financially sustainable.
Sustainability
Edge computing contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing energy consumption and optimizing resource usage. Many edge devices are low-energy, battery-powered, and perform real-time processing to eliminate waste.
Organizations can adjust operations dynamically, right-sizing energy and resource use while scaling efficiently. This reduces carbon footprints and supports eco-friendly initiatives.
How Does It Help Businesses In The Real World?
-> Operate devices efficiently with lower energy demands.
-> Adjust processes dynamically to minimize waste.
-> Scale operations without overconsuming resources.
The Impact:
Sustainability initiatives powered by edge computing improve environmental performance while reducing operational costs, aligning businesses with modern green standards.
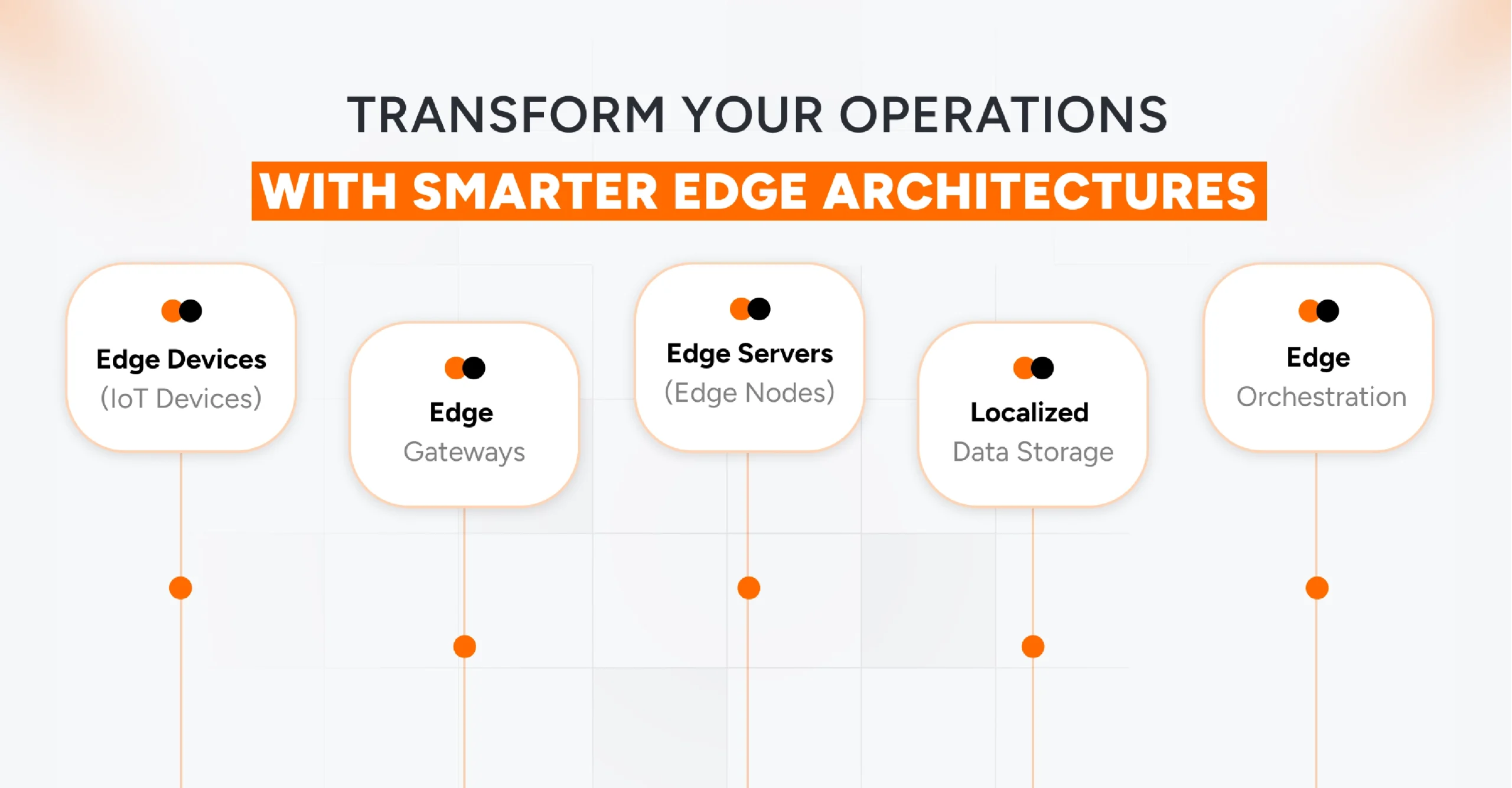
What are the Core Components of Edge Computing Architecture?
When it comes to Edge Computing in IoT, the architecture is everything. Every component plays a critical role in collecting, processing, and acting on data in real-time. Here’s a breakdown of the core pieces that make the system work seamlessly.
Edge Devices (IoT Devices)
These are the “eyes and ears” of your network, which includes sensors, actuators, and connected equipment that generate raw data. Many have basic processing power to filter and act on data locally. They capture events in real time and enable immediate actions without waiting for the cloud.
Edge Gateways
Gateways act as data traffic controllers. They aggregate information from multiple devices, filter out irrelevant data, and translate protocols. This keeps your system efficient, secure, and ensures only valuable data moves upstream.
Edge Servers (Edge Nodes)
Edge servers handle heavy lifting close to the devices. They perform advanced processing, analytics, and AI tasks locally, reducing latency and enabling near-instant decision-making. Think of them as mini data centers at the edge.
Localized Data Storage
This stores data close to where it’s generated, reducing latency and bandwidth use. It enables fast access for critical applications and keeps sensitive information secure without requiring everything to be sent to the cloud.
Edge Orchestration
Orchestration manages workloads, device communication, and application deployment across edge nodes. It ensures resources are balanced, tasks are automated, and the system runs efficiently at scale.
Network Layer
The network layer connects devices, gateways, edge servers, and the cloud. It ensures smooth data flow, low latency, and high reliability, preventing bottlenecks and maintaining a responsive IoT ecosystem.
Security Layer
Security is embedded at every level, including encryption, authentication, and access control. Edge computing minimizes exposure, protects sensitive data, and ensures compliance while supporting safe operations.
Application Layer
Applications turn processed edge data into actionable insights. They provide dashboards, alerts, and automation, enabling businesses to make smarter decisions and respond quickly to changing conditions.
Conclusion
Edge computing is revolutionizing the way businesses leverage IoT, bringing data processing closer to the source, reducing latency, improving security, and enabling real-time decision-making. From faster insights to scalable infrastructure, the benefits are undeniable for any organization looking to stay ahead in a connected world.
At AQe Digital, we help businesses implement smarter, more efficient systems that drive growth and innovation, leveraging the full potential of edge computing in IoT. Contact us today and let our experts help you design and deploy an edge computing solution tailored to your business needs.
FAQs
Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source, as well as your IoT devices. Instead of sending every bit of data to a cloud server, edge computing analyzes critical information locally. This reduces latency, improves performance, and enables real-time decision-making across connected devices.
IoT devices continuously generate massive amounts of data. Edge computing ensures that essential data is processed immediately, reducing delays, conserving bandwidth, and enabling devices to respond more quickly. It’s especially crucial for time-sensitive applications, such as autonomous systems or industrial automation.
By processing sensitive data locally, edge computing strengthens data security management by reducing the amount of information sent over networks, lowering the risk of breaches. It also allows businesses to enforce encryption, access controls, and compliance measures closer to the data source.
Absolutely. By processing data locally, businesses can minimize cloud storage and bandwidth costs. They also reduce dependence on heavy cloud infrastructure while maintaining high performance and scalability, making IoT deployments more cost-effective.
Edge infrastructure enables organizations to add more devices and handle increasing data volumes without compromising system performance. It ensures IoT deployments can grow seamlessly as business needs expand.