Cybersecurity risks have increased with the introduction of technologies like artificial intelligence. Cyber attackers are now using AI to create deepfakes and personalize phishing attacks. Plus, organizations lack security measures to counter such attacks. According to PWC’s 2026 Global Digital Trust Insights, only 6% of organizations have security measures in place to address cybersecurity risks.
This makes cybersecurity risk management crucial for organizations across industry domains. However, managing cybersecurity risks is complex and needs strategic frameworks to ensure data security. Dealing with the cybersecurity threats, ensuring proper cloud configurations, coping with changing regulatory requirements, and the cost of data recovery can be overwhelming.
To reduce the complexity of cybersecurity risk planning and implementations, our team of experts has created this resource. It covers everything from what cybersecurity risk management is and why you need it to the types of threats, the risk management process, and the frameworks. So, let’s get started.
What is Cybersecurity Risk Management?
Cybersecurity risk management is a process of continuously identifying, assessing, and responding to threats to digital infrastructure. It includes evaluating the potential impact of cyberattacks on systems, applying security controls, and mitigating risks. The primary purpose of cybersecurity risk management is to ensure the security of an organization’s data and, consequently, maintain its users’ trust.
Why Cybersecurity Risk Management Is Vital for Organizations?
Advancements in technologies such as AI, mobility, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) have transformed the way enterprises conduct business. However, such innovations also increase the risk of cybersecurity attacks.
For example, AI is an innovation that works on both sides of the cybersecurity spectrum. It enables enterprises to improve data security. At the same time, attackers use AI to design phishing attacks that can impact enterprise data.
However, it’s not just AI that attackers are using to gain access to sensitive business information. Attackers employ various tactics, including social engineering practices, API attacks, and the exploitation of IoT devices. According to a report, 67% of organizations experience IoT attacks annually. So, there is no denying the need for strategic cybersecurity risk management for your enterprise in 2026.
Some of the key reasons for your enterprise to plan cybersecurity risk management are,
1. Need for Data Security
The need for data security management is intensifying as digital operations become increasingly complex and sophisticated. With the widespread deployment of 5G technology, users have more access to faster internet speeds. This has increased the total number of users worldwide with internet access. With millions of users, data volumes have surged to a point where security is increasingly complex.
This is why, as an enterprise, you need to have a thorough cybersecurity risk management plan. A primary goal of this plan will be to address key data security needs.
2. Complex Data Environments
Irrespective of the domain your business belongs to, the complexities of data environments persist. Therefore, whether you are a 100% digital business, such as an online payment service, or a hybrid company, such as a supply chain business, you will encounter heterogeneous data environments. Maintaining data security across these environments requires effective cyber risk mitigation strategies.
3. Changing Regulatory Requirements
Data regulations evolve, with new laws and standards being introduced periodically. As an enterprise, you need to comply with these standards. Take, for example, the recent changes to GDPR guidelines, which introduced a new category of companies for compliance purposes. The small mid-caps are companies with fewer than 750 employees, a turnover of up to €150 million, or total assets of up to €129 million.
This categorization allows almost 38,000 companies to opt out of compliance guidelines. However, as an enterprise with more than 750 employees, you must ensure compliance with EU rules, especially when conducting operations in the region. Similarly, there are data regulation standards, such as HIPAA security rule and PCI DSS, among others, that you need to consider before creating a cybersecurity risk management plan.
4. Data Recovery Costs
Data recovery costs are increasing due to the growing attack surface and the complexity of identifying the root cause of these attacks. According to Sophos, the average cost of data recovery for businesses across sectors is $2.73 million. A comprehensive cyber risk management strategy can help you reduce your data recovery costs.
5. Changing Operational Environments
The complexities of hybrid work environments, heterogeneous networks, and systems can pose significant cyber risks. Take an example of a healthcare service provider that offers virtual consulting. Patients interact with the clinician via devices connected to the local network. These local networks are vulnerable to cyberattacks, which can result in patient data breaches.
As an enterprise offering services that require the exchange of sensitive data, you need a cybersecurity risk management plan that considers both external and internal factors.
Now that you know why cybersecurity risk management is crucial for your organization, it’s time to understand the risks and threats.
What are the Major Cybersecurity Threats for an Enterprise?
From AI-powered cyberattacks to cloud security breaches, ransomware, and deepfake fraud, there are numerous types of threats.
Some of these cybersecurity threats are,
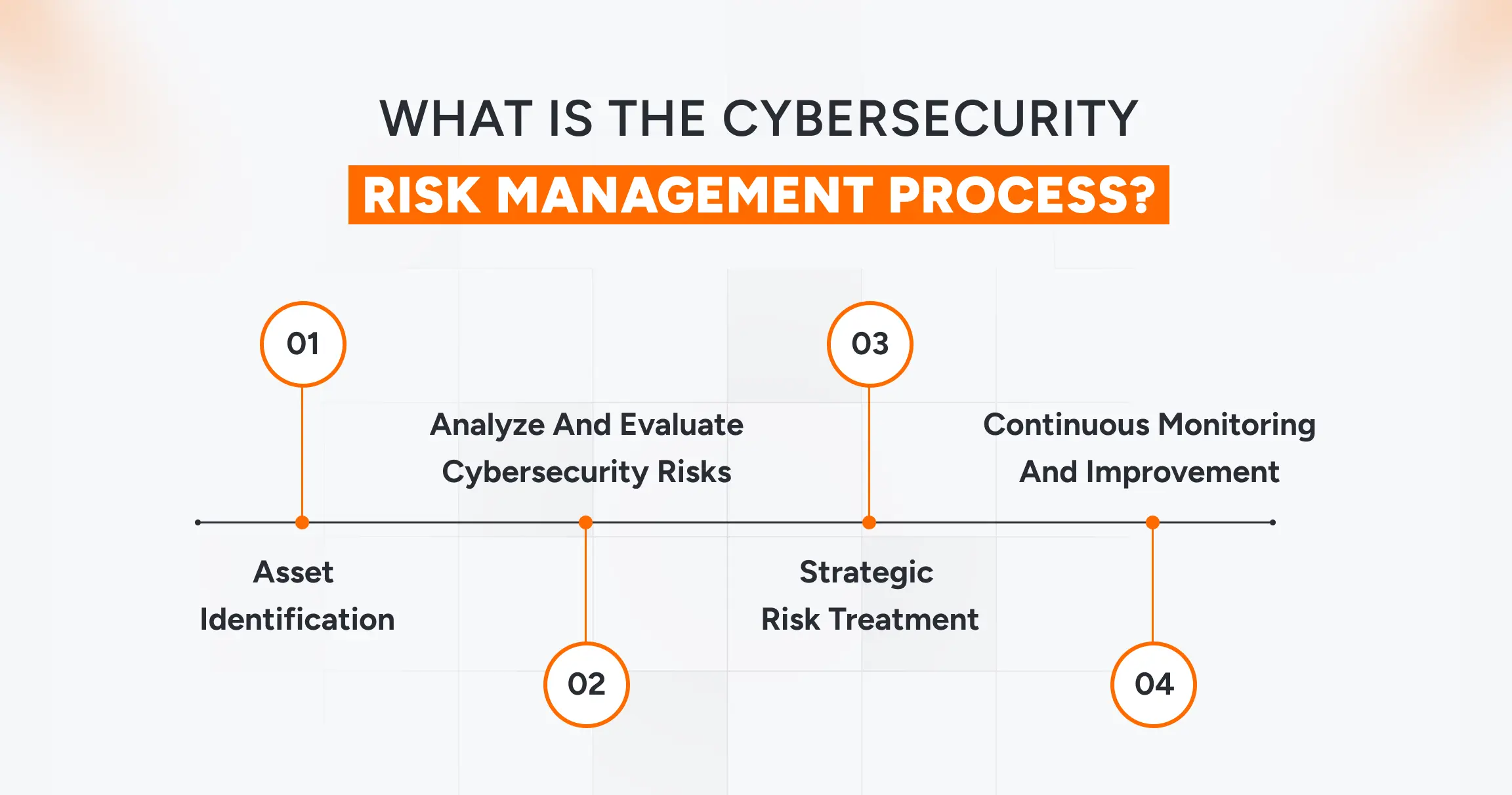
What is the Cybersecurity Risk Management Process?
The cybersecurity risk management process includes steps such as asset identification, risk evaluation, strategic risk treatment, and ongoing monitoring.
1. Asset Identification
This step involves identifying key assets for your organization by delineating those that would be affected by a cyberattack. Such assets can be hardware, software, or data systems. Identify the assets you want to prioritize for security testing and categorize them by the level of data protection they require. You can leverage security and compliance solutions for automated testing.
2. Analyze and Evaluate Cybersecurity Risks
Once assets are identified, the next step is to assess the potential risks associated with each asset. This involves determining the likelihood of various cyber threats and their potential impact on your organization. Use both qualitative and quantitative risk measurement methods to rank risks for decision-making.
Key activities in this stage include:
- Identifying threat sources, including malware, phishing, insider threats, and ransomware.
- Understanding vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and applications.
- Estimating the probability of exploitation for each vulnerability.
- Calculating potential financial, operational, and reputational impacts.
3. Strategic Risk Treatment
After evaluating risks, select the most appropriate risk treatment strategies to reduce exposure. Risk treatment involves selecting measures to mitigate, transfer, avoid, or accept risks based on their severity and your organizational priorities.
Key actions include:
- Implementing security controls such as firewalls, encryption, and multi-factor authentication.
- Outsourcing risk via cyber insurance or third-party services.
- Discontinuing or altering processes that carry unacceptable risk.
- Accepting low-level risks with documented business justification.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Cybersecurity risk management is not a one-time activity. Continuous monitoring ensures new threats are detected and controls remain effective over time. This process integrates threat intelligence, logging, and performance reviews into ongoing operations.
Ongoing monitoring actions include:
- Tracking security incidents and response effectiveness.
- Reviewing and updating security policies quarterly or annually.
- Conducting vulnerability scans and penetration tests on a regular schedule.
- Integrating threat intelligence feeds to anticipate emerging risks.
What are Key Cybersecurity Risk Management Frameworks?
Effective cyber risk management relies on choosing a structured framework that guides your organization from governance and assessment to ongoing monitoring and response. These frameworks help standardize processes, meet regulatory expectations, and enable consistent improvement—critical as threats and compliance requirements evolve.
Below is a comparative overview of widely adopted cybersecurity risk management frameworks:
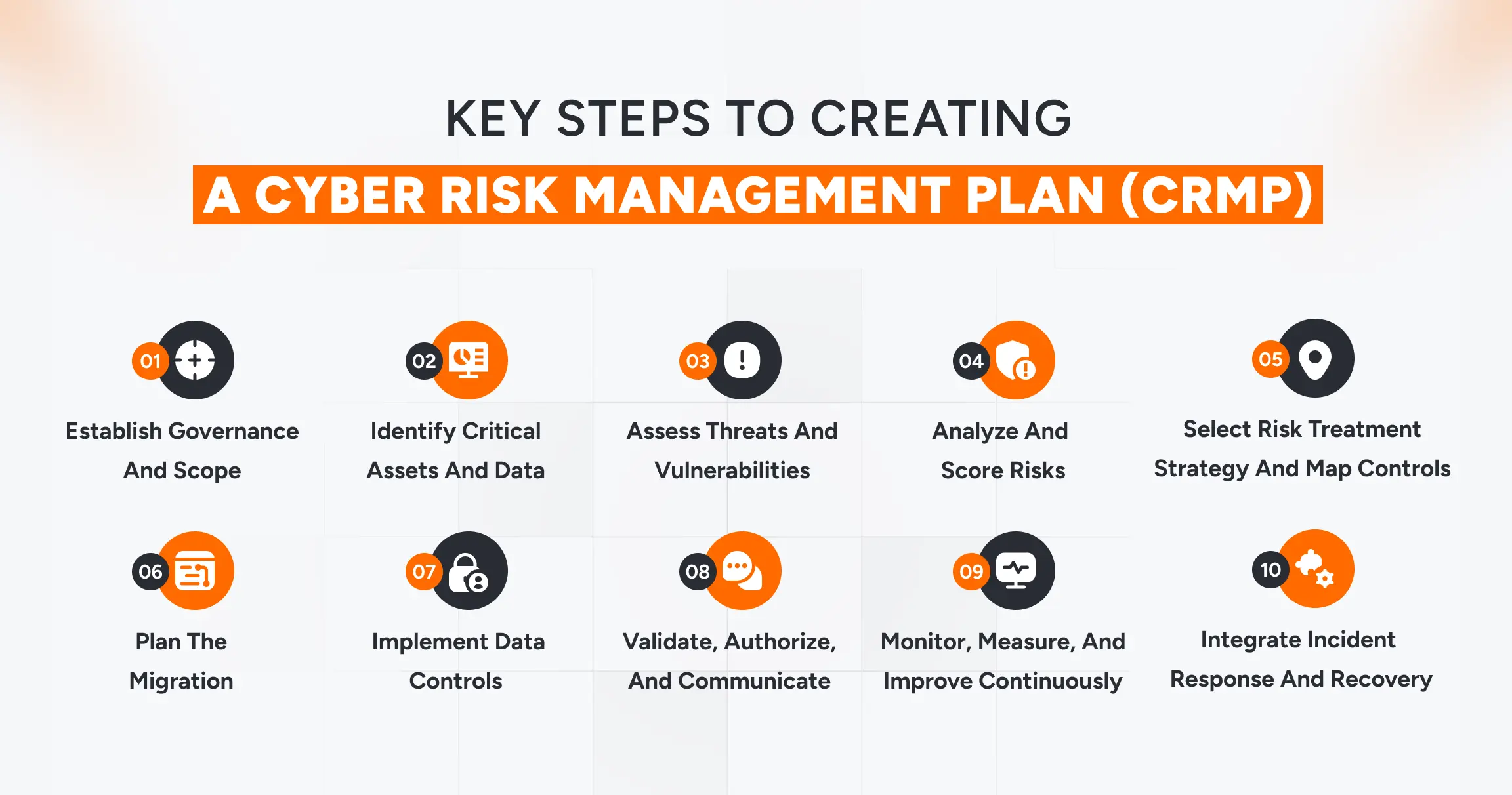
Key Steps to Creating a Cyber Risk Management Plan (CRMP)
Creating a comprehensive cybersecurity risk management plan includes establishing governance, building a complete asset inventory, analyzing risks, planning treatments, and executing a controlled migration.
Step 1: Establish Governance And Scope
A CRMP must begin with clear decision rights, risk tolerance, and scope, so that assessments and treatments align with business priorities and can be authorized within a repeatable lifecycle.
Anchor planning to NIST RMF’s Prepare step and define who owns the plan, what systems and data are in scope, and how results will be used to guide control selection and acceptance decisions.
- Define risk appetite, stakeholders, and reporting under an RMF-aligned “Prepare” activity to ensure decisions, funding, and timelines are coherent.
- Document scope, assumptions, and decision criteria for the upcoming risk assessment per SP 800-30’s “prepare” guidance to keep outputs traceable and defensible.
Step 2: Identify Critical Assets And Data
Asset identification is the foundation of a CRMP; a complete, living inventory enables risk scoring, control coverage tracking, and incident readiness.
- Use CIS Controls v8.1 asset classes to eliminate blind spots and continuously enrich inventory with ownership, sensitivity, and regulatory tags.
- Build a single repository across six CIS asset classes, like devices, software, data, users, network, and documentation.
- Ensure that each class is categorized according to its owner, criticality level, sensitivity rating, and regulatory impact assessment.
- Automate discovery (EDR/MDM, network scanners, cloud APIs, IdP, data classification) and validate entries weekly for decision-grade accuracy as the basis for risk modeling.
Step 3: Assess Threats And Vulnerabilities
Establish a practical threat baseline and a multi-method vulnerability picture to connect realistic attack paths to assets and business processes.
- Apply SP 800-30’s conduct phase to identify threat sources/events, vulnerabilities, predispositions, likelihood, and impact for each scenario.
- Utilize a straightforward model, combined with current attack patterns tailored to the organization’s size and sector, to enhance scenario realism.
- Combine automated scans, penetration tests, configuration reviews, human risk exercises, and third‑party checks with defined cadences to capture technical and human factors.
Step 4: Analyze And Score Risks
Scoring focuses attention and budget on the most consequential exposures by estimating both likelihood and impact and documenting the rationale. Keep assessments transparent and repeatable, as per SP 800-30, by recording models, inputs, and confidence levels so that re-assessment and audit traces remain strong.
Compute a simple risk score using,
Cybersecurity Risk = Likelihood of Attack × Impact on The System
Create a risk score on a 1–5 scale, then sort by business impact for prioritization.
Open a risk register capturing assets, scenarios, inherent risk, existing controls, residual risk, owners, costs, and target treatments for ongoing governance.
Step 5: Select Risk Treatment Strategy And Map Controls
Select a response for each scenario: mitigate, avoid, transfer, or accept, and align it with a risk-to-control mapping that specifies owners, budgets, and deadlines.
- Favor high-impact safeguards first (identity hardening, backups, patch hygiene, EDR/anti‑ransomware, secure email) to produce measurable early reductions.
- Build a risk-to-control table using this flow (Risk-Control-Owner-Cost-Deadline-Acceptance criteria) to track the improvements in residual risk over time.
- Use treatment modes from common practice (treatment, tolerance, termination, transferal) to ensure explicit acceptance and periodic review where risk remains.
Step 6: Plan the migration
Create a phased roadmap that sequences control rollouts, identity and network baselines, data migrations, and legacy decommissioning, with defined cutover criteria, from the current state to the target state.
- Integrate contingency planning so that every change includes tested recovery steps and explicit rollback procedures in case acceptance tests fail.
- Select, Implement, Assess, Authorize, Monitor, ensuring each wave is authorized against residual risk and business readiness.
- Embed contingency elements like BIA, RTO/RPO targets, and recovery strategies, and ensure optimal maintenance.
Step 7: Implement Data Controls
Implement prioritized administrative, technical, and physical controls in sprints, instrument logging/telemetry, and update system documentation for traceability.
- Define RACI and escalation paths to ensure responsibilities and communication are unambiguous during both normal operations and incidents.
- Document each control’s configuration, monitoring hooks, and acceptance tests, and link them back to risks in the register for end-to-end traceability.
- Publish a RACI matrix and a risk-based escalation tree to ensure decision paths remain fast and reliable under pressure.
Step 8: Validate, Authorize, and Communicate
Assess control effectiveness against planned objectives, record results and limitations, remediate gaps, and seek authorization decisions tied to residual risk and tolerance.
Tailor reporting for executives and technical teams, keeping confidence levels and known limitations explicit per SP 800‑30 communication guidance.
- Execute assessment plans, record findings, update residual risk, and capture remediation actions before finalizing authorization decisions.
- Provide audience-specific reporting and note uncertainties to support informed risk acceptance or further hardening.
Step 9: Monitor, measure, and improve continuously
Establish continuous monitoring for control health, vulnerabilities, configuration drift, incidents, and vendor risk; re-score when exposure changes.
- Adopt the guide’s cadence and KPIs, such as MTTD, MTTR, patch compliance, phishing rate, backup restore success, and control coverage, to verify value and drive PDCA cycles.
- Operate RMF Monitor with recurring scans, assessments, and incident feedback loops to keep posture current and responsive.
- Track a dashboard of KPIs and run the PDCA (Plan–Do–Check–Act) cycle after each migration wave, closing gaps and updating the risk register every month.
Step 10: Integrate Incident Response And Recovery
Complement mitigations with ready-to-execute incident response phases: detect, triage, contain, eradicate, recover, learn, and map to top threats such as ransomware.
- Sustain contingency readiness with exercises that validate RTO/RPO and improve recovery playbooks over time.
- Maintain IR runbooks aligned to the six phases and test them quarterly to ensure timely containment and restoration.
- Review post-incident lessons learned to refine controls.
Final Note
True cybersecurity resilience isn’t achieved by simply reacting to threats. It’s built on a proactive, framework-driven strategy that evolves with your business and the digital landscape. Leveraging robust risk management frameworks empowers your organization to go beyond mere compliance and actively defend its data, reputation, and future growth.
Suppose you’re ready to move beyond uncertainty and lead with confidence. Partner with AQe Digital. Unlock our expert-led risk assessments and custom security solutions designed to keep your business a step ahead of cyber threats. Don’t just minimize risk, secure your advantage. Contact cybersecurity experts at AQe Digital and transform your security posture today.
FAQs
Cybersecurity risk management involves identifying, assessing, and responding to risks across your digital infrastructure. It is crucial because advances in AI, cloud, and IoT have made businesses more vulnerable to sophisticated threats. Without a strategic risk management plan, organizations face growing challenges with data protection, regulatory compliance, and recovery costs.
Major cybersecurity threats include AI-powered phishing and deepfakes, ransomware attacks, cloud misconfigurations, IoT device exploits, and insider threats. These attacks can cause data breaches, financial loss, operational outages, and reputational damage. Proactive controls and continuous monitoring are vital to counter these evolving risks.
New regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS set strict data protection standards for organizations worldwide. A robust cybersecurity risk management plan should align with these requirements, helping businesses avoid legal penalties and ensure secure operations. Keeping track of evolving guidelines is key to maintaining compliance.
The process covers asset identification, risk analysis, risk treatment (mitigation, transfer, avoidance, acceptance), and continuous monitoring. Each step ensures organizations recognize key assets, assess vulnerabilities, implement strategic controls, and adapt their posture as threats change. Downloadable templates streamline planning and execution.
Widely used frameworks include NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF), CIS Controls, ISO/IEC 27001, and COBIT. These frameworks provide structured approaches for governance, assessment, control selection, and ongoing improvement, helping businesses build resilient, compliant, and scalable security strategies.