Over 91% of businesses with more than 11 employees use a CRM to manage customer relationships and sales pipelines. It’s a clear sign that companies rely heavily on CRMs to organize customer interactions and keep sales on track.
However, CRMs don’t give you the whole picture. They capture what your teams put in not necessarily what your customers actually do. That’s why Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) are becoming the next big thing, with the market expected to hit USD 7.39 billion by 2028.
So, while CRMs help you manage customer connections, CDPs help you truly understand customer behavior. For brands investing in retail IT solutions, this difference can define how well they personalize experiences, predict customer needs, and foster loyalty.
Let us break down CDP vs. CRM to see how each system handles data and what sets them apart.
What is a CRM?
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is your go-to tool for managing and nurturing relationships with existing customers.
It helps retail teams stay organized, track interactions, and deliver better service — especially across sales and customer support.
In simple terms, a CRM helps you:
- Store and manage customer details, including names, contact information, and purchase history.
- Track communication history (emails, calls, chat logs, etc.).
- Manage loyalty memberships and follow-ups.
- Support marketing and sales teams with better visibility into customer needs.
For example, if your customer bought running shoes last month, your CRM can:
- Send them a reminder about a loyalty discount.
- Suggest related accessories, such as socks or shoe cleaners.
- Help your store associate personalize the next interaction.
In short, a CRM helps you know who your customers are and what your team has done to engage them. But it relies on manually entered or known data, and doesn’t automatically track behavior across all touchpoints.
What is a CDP?
A Customer Data Platform (CDP), on the other hand, takes things to the next level.
When comparing a CDP vs CRM, think of a CDP as your data hub. It automatically collects, unifies, and activates customer data from every retail channel in real time.
A CDP helps you:
- Collect customer data from multiple sources, including website, app, in-store POS, social media, and ads.
- Unify all that data to create a single customer profile (even from anonymous visitors).
- Analyze behavior to predict intent, preferences, and buying patterns.
- Activate personalized campaigns based on real-time insights.
For example:
A shopper browses jackets on your app, abandons the cart, then visits your store two days later. A CRM wouldn’t connect these actions. A CDP would, and could trigger an automatic “special offer” email or in-app notification.
What is CDP vs CRM? – The Core Difference
Both CDP and CRM systems center on customer data, but the way they collect, process, and use it is fundamentally different.
A CRM system is designed to manage interactions with known customers. For example, a CRM for eCommerce helps store contact information, track purchase history, log support requests, and give sales and service teams a clear view of each customer. It’s focused on what your team knows about the customer and how they interact with your business across channels.
For retailers, this means following up on a loyalty program, sending a discount reminder for a previously purchased product, or tracking an in-store inquiry.
On the other hand, CDPs provide retailers with a 360-degree customer view by connecting marketing and shopping behavior. CRMs offer a more focused, interaction-based view, centered on relationship tracking.
CDP handles first-party, second-party, and third-party data at scale, encompassing both structured and unstructured data. It includes web analytics, session data, and behavioral signals. If your data contains millions of customer touchpoints, only a CDP can efficiently manage and unify it.
Another key distinction is that a CDP collects and unifies customer data across all channels, both online and offline. It automatically gathers information from your eCommerce site, mobile apps, in-store POS systems, marketing campaigns, and even third-party sources.
This creates a single, complete customer profile that includes both known and anonymous behaviors. For retailers, this unified view is crucial for understanding how shoppers move across channels, what they are interested in, and what triggers purchases or abandonment.
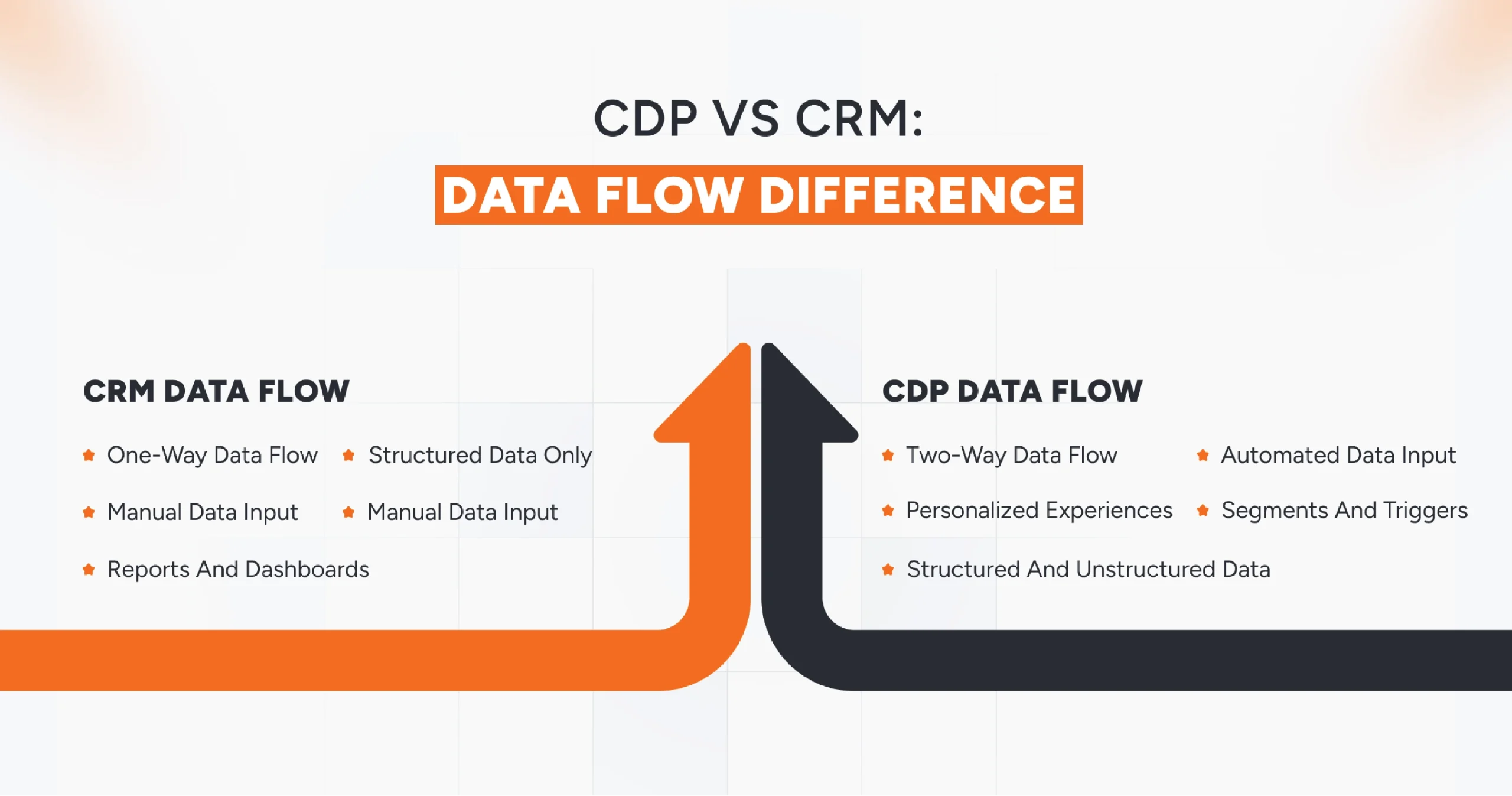
CDP vs CRM: How Data Flows Differ
The difference between CDP and CRM becomes clearer when you examine how data flows within each system. Both handle customer information, but a CRM stores it, while a CDP activates it.
CRM Data Flow
A CRM system is designed to store and manage structured, historical data. It relies on manual inputs and team updates.
- Direction: One-way, from teams to the system.
- Source: Sales, support, or marketing teams enter customer details, transaction history, and communication logs.
- Data Type: Structured data names, contact info, purchase records, service tickets.
- Purpose: To manage ongoing relationships, monitor pipelines, and track loyalty interactions.
- Output: Reports and dashboards that guide human decisions, but no automatic data sharing or activation.
Example:
A store manager updates the CRM after a customer uses loyalty points or requests a product exchange. The record helps future interactions but doesn’t trigger immediate marketing actions.
CDP Data Flow
A CDP (Customer Data Platform), in contrast, is built for continuous, automated data movement. It connects online and offline touchpoints in real time.
- Direction: Two-way, data flows in and out seamlessly.
- Source: E-commerce sites, POS systems, apps, ad platforms, social media, and third-party tools.
- Data Type: Structured and unstructured – behavioral, transactional, and event-driven.
- Purpose: To unify data, create real-time customer profiles, and activate personalized experiences instantly.
- Output: Segments, triggers, and insights that feed marketing automation, analytics, and AI models.
Example:
When a shopper abandons a cart online, the CDP identifies them, updates their profile, and instantly triggers an automated push notification or email with relevant product suggestions.
Key Benefits: CDP vs CRM
Choosing Between CDP and CRM: What Fits Your Business Best?
Every retail business reaches a point where managing customer relationships and data becomes a challenge. The right solution, CDP, CRM, or a combination of both, depends on your goals, data maturity, and customer engagement model.
When to Choose a CDP
A Customer Data Platform is best suited for businesses that:
- Operate across multiple online and offline channels, struggling with disconnected data.
- Need a unified customer profile that updates in real time.
- Want to personalize marketing at scale based on behavioral, transactional, and demographic insights.
- Depend heavily on automated campaigns, loyalty programs, and predictive analytics to drive growth.
- They are data-rich but insight-poor; they collect information but lack actionable intelligence.
Example:
A retail chain with both eCommerce and physical stores uses a CDP to connect POS, web analytics, mobile app data, and social engagement. This creates a 360° view of every shopper for personalized offers.
When to Choose a CRM
A Customer Relationship Management system is ideal if your business:
- Focuses primarily on sales management and customer retention.
- Needs to track leads, opportunities, and post-purchase interactions in one place.
- Has a limited number of customer touchpoints and a more direct engagement model.
- Prioritizes relationship nurturing over large-scale marketing automation.
- Aims to streamline team workflows and maintain accountability across departments.
Example:
A niche fashion retailer or B2B wholesaler benefits from CRM by tracking every client conversation, managing leads efficiently, and fostering strong service relationships.
When You Need Both CDP and CRM
In most modern retail ecosystems, combining both delivers the real advantage. A CDP + CRM integration creates a seamless data-to-action pipeline.
You need both if your business:
- Operates in a data-intensive environment but also relies on intense customer engagement cycles.
- Wants marketing and sales alignment, with customer data insights directly driving personalized outreach.
- Handles omnichannel operations, requiring both data unification (CDP) and relationship management (CRM).
- Aims to enhance customer lifetime value (CLV) through more profound insights and continuous engagement.
- Seeks to future-proof customer experience by integrating AI, automation, and predictive analytics.
Example:
A national retailer combines CDP and CRM: the CDP captures data across channels, while the CRM helps sales and service teams act on those insights. This results in faster conversions, better retention, and higher customer satisfaction.
When to Choose CDP, CRM, or Both
Common Challenges in Integrating CDP or CRM
Integrating Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) or Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems can transform how businesses understand and engage with customers. But many retailers face roadblocks that can slow down ROI and adoption.
1. Disconnected Data Sources
Customer information is scattered across POS systems, eCommerce platforms, apps, and social platforms. Without a clear integration plan, it’s tough to build a single, reliable customer view.
2. Inconsistent Data Quality
Duplicate or outdated customer records lead to poor insights and wasted marketing efforts. Clean, standardized, and regularly updated data is essential.
3. Legacy System Barriers
Older systems often lack modern APIs, making integration and real-time syncing difficult. This slows down how quickly teams can act on customer insights.
4. Poor Team Alignment
Sales, marketing, and service teams often work in silos. Without shared goals and collaboration, even the best CDP or CRM can underperform.
5. Overcomplicated Setup
Many businesses underestimate the extent of customization and configuration these platforms require to fit specific processes. A clear roadmap helps avoid implementation delays.
6. Cost and Resource Pressure
Licensing, data storage, and expert implementation can add up fast. Without a defined ROI strategy, costs can outweigh short-term benefits.
7. Compliance and Privacy Issues
Managing customer consent and data under regulations like GDPR or India’s DPDP Act can be complex. Any oversight risks, penalties, and trust issues.
How AQe Digital Simplifies CDP and CRM Integrations
Our experience in CRM consulting services spans various industries, including projects such as CRM consulting for construction engineering, where we helped teams streamline data, enhance collaboration, and make informed decisions with confidence.
With AQe Digital, integration isn’t just a technical task. It’s a way to give your teams clarity, your customers better experiences, and your business the edge to stay ahead in today’s competitive market.
Here’s how we ensure seamless CDP and CRM integration:
- Data Mapping and Audit
- Custom Integration Architecture
- Data Cleansing and Transformation
- Real-Time Activation
- Monitoring and Compliance
Our solutions simplify processes, giving your teams the clarity to act faster.
Conclusion
Choosing the right system or the right combination can transform how your business understands and engages with customers. By clearly distinguishing the roles, benefits, and applications, retailers and enterprises can make smarter, data-driven decisions. Connect with us for proper guidance.
With us, integrating your systems becomes seamless, turning scattered data into actionable insights. The result is stronger customer relationships, faster decision-making, and measurable business growth that keeps your teams and customers aligned and engaged.
FAQs
Yes, integrating CDP vs CRM systems allows businesses to combine behavioral insights with relationship management. This ensures personalized engagement, timely follow-ups, and proactive support, significantly improving customer retention.
With a Customer Data Platform (CDP) versus a CRM, businesses can segment audiences, track behavior, and personalize campaigns more effectively. A CDP delivers real-time data, and a CRM ensures structured communication and relationship management, boosting marketing ROI.
The primary difference between CDP and CRM lies in how they manage data versus how they interact. A CDP provides insights to target high-potential customers, while a CRM manages the sales process, helping teams close deals more efficiently.
A CDP is scalable for businesses of all sizes. Even small companies can benefit from a unified customer view, enabling smarter decisions, better segmentation, and more effective use of their CRM data.
Both CDP and CRM systems prioritize data security. Still, a CDP is designed to consolidate data from multiple sources, so implementing strict governance and compliance policies is crucial to protect sensitive customer information.
Results depend on the strategy and the quality of integration. With the right setup, businesses can leverage CDP vs. CRM insights to improve targeting, personalize campaigns, and achieve better sales outcomes within weeks to months.