Adoption of generative AI models has reached a decisive inflection point. The era of experimental pilots is effectively over. Because the market has shifted to strategic, enterprise-scale deployments, with 33% of organizations already deploying agentic AI systems, this includes moving beyond simple answer engines, implementing autonomous agentic workflows, and demanding complex execution capabilities.
Choosing an enterprise LLM is now a critical risk calculation. Performance gaps between Anthropic and OpenAI, and between Gemini and OpenAI, have become highly task-specific. This means enterprises need to evaluate these platforms based on rigorous data security, regulatory governance, and scalable infrastructure.
This article, however, is your guide to the ultimate enterprise model selection for generative AI. It compares LLM providers such as Anthropic, Gemini, and OpenAI through a strict enterprise lens to guide investment strategies for the 2026 fiscal year.
What Makes a Generative AI Model “Enterprise-Grade”?
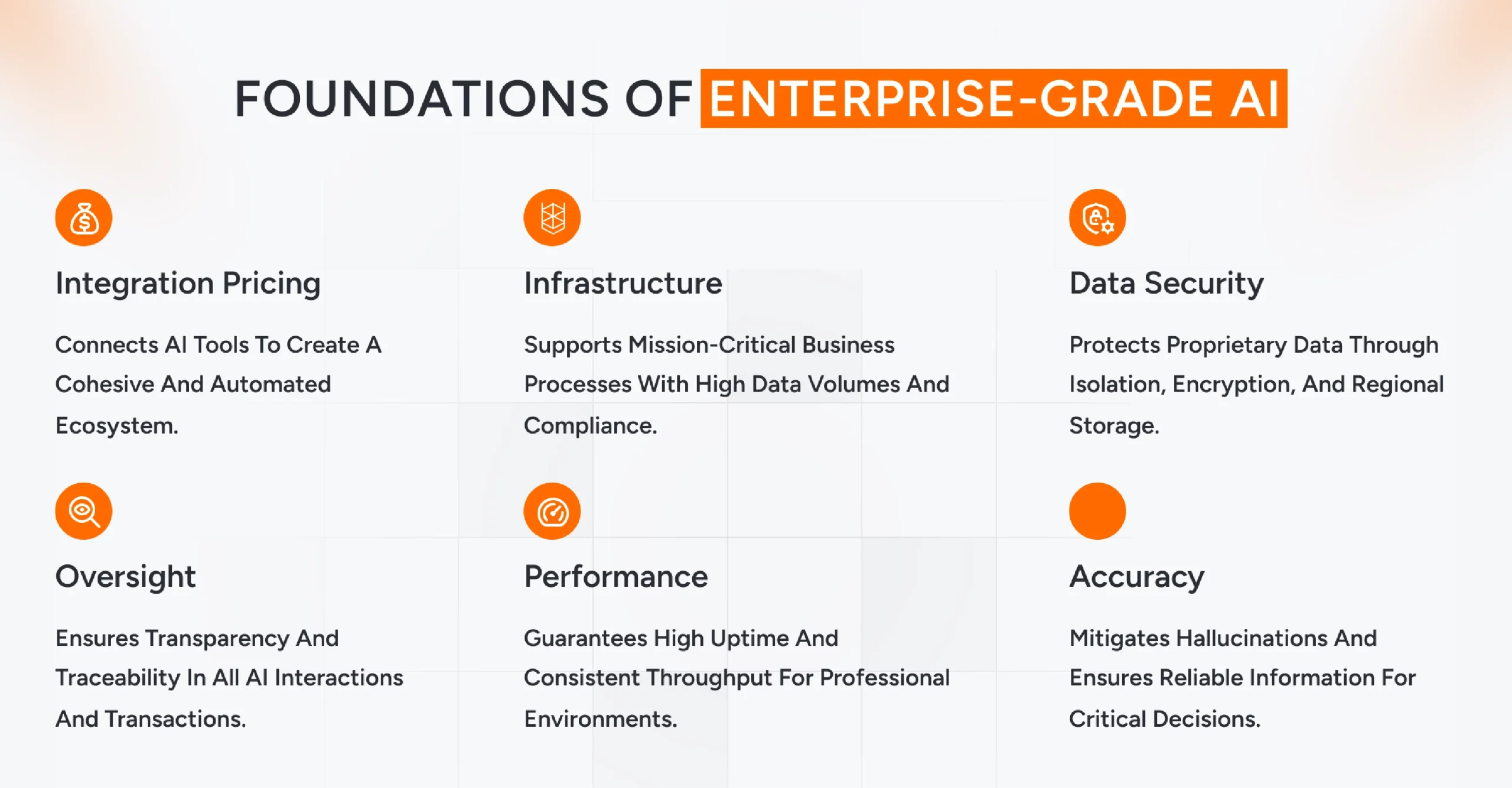
A generative AI model is considered “enterprise-grade” when it evolves from an experimental interface into a foundational, secure, and reliable pillar of corporate infrastructure. Enterprise-grade platforms are designed to support mission-critical business processes by processing massive volumes of data within strict compliance boundaries.
The key characteristics that define enterprise-grade generative AI include:
1. Enterprise-Grade AI Is Your Infrastructure
An enterprise-grade AI systems platform supports mission-critical business processes. It processes massive data volumes, strictly adheres to compliance standards, and secures your operations.
2. Your Proprietary Data Stays Yours
The barrier to adoption is data security, because a single breach can erode customer trust. This includes strict isolation of training data, advanced encryption such as AES-256, and sovereign regional storage options.
3. Oversight Is Not Optional
Transparency is required for every user interaction, data exchange, and financial transaction on your enterprise platforms. Regulators across industries now demand traceability, which covers alignment with SOC 2 standards, comprehensive time-stamped logs, and granular role-based access controls.
4. “Best-Effort” Performance Fails the Business
Unreliable uptime disrupts professional environments. Because latency kills productivity during peak traffic, this guarantees 99.9% uptime, provisioned throughput for consistency, and 24/7 priority support access.
5. Accuracy Drives Critical Decisions
LLM Models must mitigate hallucinations in high-stakes fields. Because false information creates legal liability. This utilizes Retrieval-Augmented Generation, automated triple-check verification, and inline citations for explainability.
6. Integration Completes the Ecosystem
Standalone tools simply create silos. Because automation requires coherence This means seamless API integration, fine-tuning on domain data, and end-to-end orchestration of complex tasks.
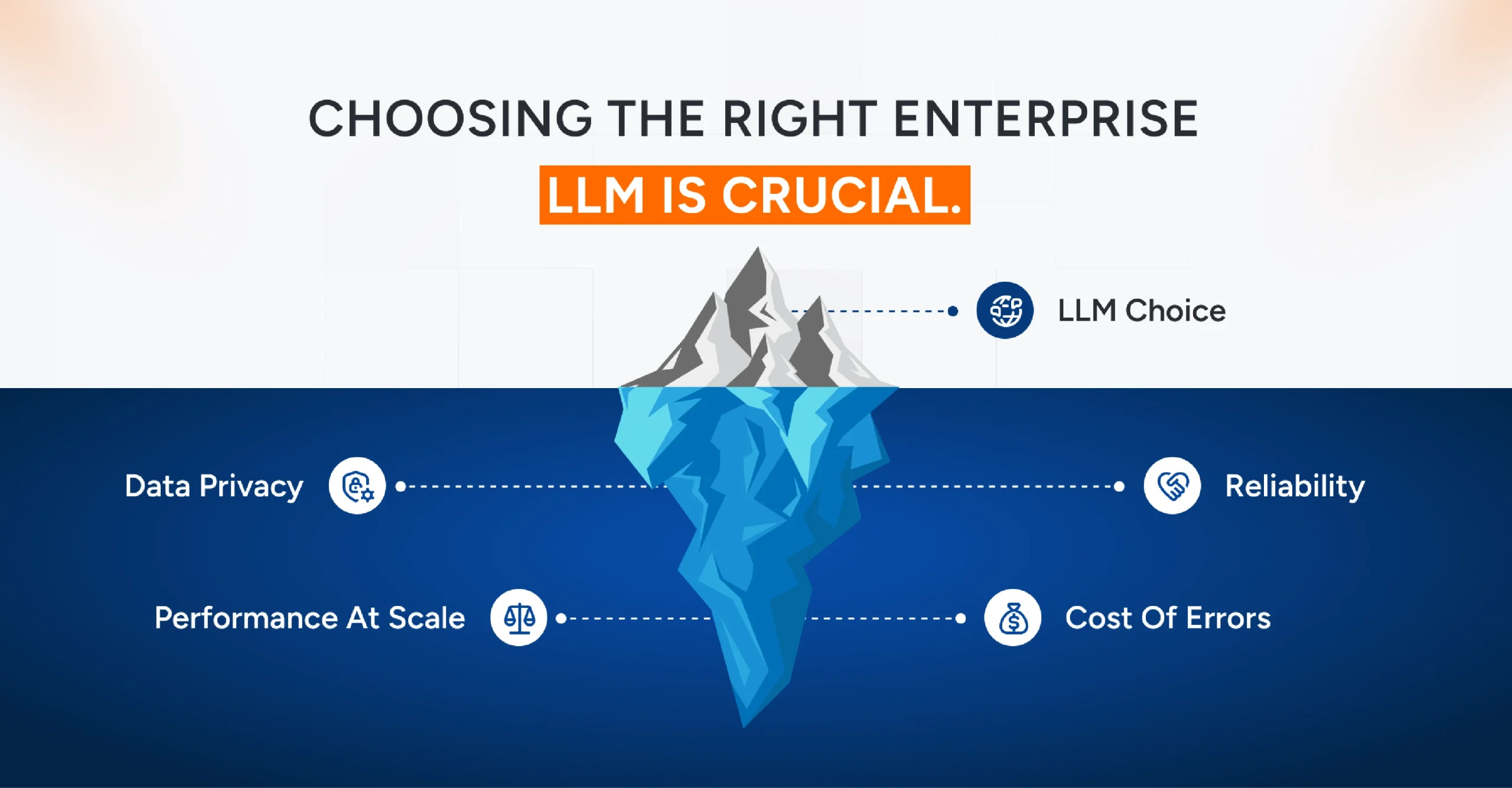
Why Choosing the Right Enterprise LLM Matters?
An Enterprise LLM functions as your execution layer. Not just an answer engine. Accurate business intelligence requires access to your company’s entire knowledge base. This includes deep integration into workflows, agentic capability to execute tasks, and strict operational control.
Why Not All Models Qualify
A model might be fluent but operationally reckless. Consumer tools often lack the necessary architectural safeguards. What this means is you risk training future models with your secrets, suffering high hallucination rates, and exposing systems to adversarial injection attacks.
Prioritizing Data Privacy
Data Privacy is your foundational requirement. Because regulatory mandates are unforgiving, this requires enterprise key management, geographic data zones, and zero-retention policies that prevent vendors from accessing your data.
Ensuring Performance at Scale
Relying on standard API limits invites failure. Because shared infrastructure creates a “noisy neighbor” effect, this includes provisioned throughput units, consistent latency guarantees, and efficient context caching for high-volume operations.
Demanding Reliability
The distinction between Anthropic and OpenAI often centers on this safety philosophy. Because a model that guesses is a liability, this involves constitutional AI training, epistemic humility to avoid hallucinations, and comprehensive audit logs for compliance.
Counting the Cost of Errors
A comparison of Gemini vs OpenAI reveals significant differences in integration value and cost efficiency, as unoptimized models rapidly drain IT budgets. This results in financial inefficiency, fragmented operational silos, and the catastrophic cost of a data breach.
High-Level Overview of Modern Generative AI
The landscape has shifted from experiment to execution. Modern generative AI models are no longer simple answer engines. Because the technology now functions as a reasoning engine and execution layer. This includes extended thinking capabilities, internal reasoning chains to verify logic, and simultaneous multimodal processing.
Foundation Models vs. Task-Specific AI
Distinguishing between capabilities is critical for ROI. Foundation models serve as the ecosystem’s “brain.” Because they handle unstructured data, ambiguity, and complex orchestration, this means leveraging massive context windows, solving abstract problems, and managing heavy computational loads.
But task-specific AI drives efficiency. High-volume operations cannot rely on expensive generalist models because speed and cost dictate production viability. This includes deploying “Flash” variants for low latency, specialized code generation, and targeted image editing.
The Rise of Multi-Model Strategies
Single-vendor reliance is a strategic failure point. An effective Enterprise LLM strategy demands a multi-model approach. Because no single model dominates every performance benchmark, this requires intelligent prompt routing to reduce costs, avoid vendor lock-in, and ensure redundancy during outages.
Leading Providers: Distinct Philosophies
Anthropic (Claude)
Reliability defines the Anthropic proposition. Their “Constitutional AI” prioritizes safety over raw speed. Because epistemic humility prevents dangerous hallucinations, it includes superior coding performance, high resistance to prompt-injection attacks, and strict adherence to auditability requirements in regulated industries.
OpenAI (GPT)
Reasoning density drives the OpenAI advantage. The Anthropic vs OpenAI decision often hinges on raw logic versus safety constraints. Because their models act as holistic reasoning engines, this includes deep integration with the Microsoft Foundry, dominance in abstract mathematics, and context-aware planning for professional workflows.
Google (Gemini)
Ecosystem ubiquity distinguishes Gemini. The Gemini vs OpenAI comparison is defined by native multimodality. Because the model processes text, video, and audio simultaneously without conversion, what this means is massive context retrieval, real-time search grounding, and seamless execution across Google Workspace.
Anthropic vs. OpenAI: Core Differences for Enterprises
You must choose between competing developmental philosophies. The Anthropic vs OpenAI divide represents a split between rapid innovation and strictly governed reliability. Because OpenAI pursues a “capability-first” strategy to push the boundaries of what is possible.
This includes deploying frontier multimodal features, accelerating broad market adoption, and managing risks through retrospective preparedness frameworks.
In contrast, you prioritize safety with Anthropic’s “Responsible Scaling.” Their approach focuses on solving alignment challenges before releasing new capabilities. Because a model is useless if it cannot be trusted. This means prioritizing helpfulness, honesty, and harmlessness over raw speed or feature density.
Alignment and Hallucination Handling
Anthropic utilizes “Constitutional AI” to embed safety principles directly into the training process. Because “epistemic humility” ensures the model admits uncertainty rather than inventing facts. This includes superior resistance to prompt injection attacks, lower hallucination rates in high-stakes tasks, and strict adherence to safety protocols.
But OpenAI is closing the reliability gap. Their generative AI models now employ “System 2” thinking to reduce errors. The model generates internal reasoning chains to verify logic before answering. What this means is significantly improved performance on math and logic tasks, though often with a different risk profile regarding adversarial attacks.
Enterprise Trust and Governance
Anthropic positions itself as the trusted leader for regulated sectors. Because they offer explicit “zero data retention” policies that guarantee your inputs never train their models. This includes strict safety thresholds for model release, rigorous cost attribution via inference profiles, and keeping data within your private cloud environment.
OpenAI counters with robust infrastructure integration. Their governance strategy relies on deep ties to Microsoft. Because enterprises need mature controls like provisioned throughput and geographic compliance zones, this involves immutable compliance logs, time-windowed audit trails, and seamless integration with existing corporate identity systems.
Optimizing Use Cases
You should deploy a multi-model strategy to maximize distinct strengths. The enterprise LLM landscape requires routing tasks based on specific architectural advantages. Because relying on a single provider creates operational blind spots.
This includes using Anthropic for complex coding and legal review, leveraging OpenAI for generalist reasoning and creative content, and utilizing prompt caching to manage heavy text processing costs.
Gemini vs. OpenAI: How Google’s AI Competes at Enterprise Scale?
The value of Google’s proposition lies in the deployment architecture. Enterprise LLM adoption relies less on the model itself and more on the secure infrastructure wrapping it, because Vertex AI transforms a simple chatbot into a deterministic business component.
This includes grounding responses in real-time Search data, ensuring predictable costs via provisioned throughput GSUs, and eliminating “copy-paste fatigue” by analyzing Drive files directly within the security boundary.
Strengths in Multimodal and Data-Heavy Workflows
Google competes by prioritizing massive information ingestion. The Gemini vs OpenAI battle is defined by the difference between context breadth and reasoning density. Native multimodality allows the processing of video, audio, and text simultaneously without transcription.
This includes handling 2-million-token context windows, analyzing hours of raw meeting footage, and executing complex retail transactions via the “Universal Commerce Protocol.”
Suitability for Enterprises Standardized on Google
Existing infrastructure commitments often dictate the final choice. For organizations already embedded in the Google ecosystem, the integration friction is nonexistent.
What this means is immediate productivity gains, seamless Workspace access, and cost efficiencies, with Gemini Flash prices dropping significantly below competitors’ for high-volume batch operations.
Trade-offs Compared to OpenAI’s Ecosystem
Distinct architectures necessitate a trade-off analysis. While Google leads in context, OpenAI maintains the advantage in pure logic and developer maturity. Because generative AI models like GPT-5.2 excel at abstract problem solving and “reasoning density.”
This includes superior performance on math benchmarks, a broader “full stack” developer toolbelt for agentic loops, and the rigorous geographic governance controls provided by Microsoft Foundry.
Enterprise Evaluation Criteria: How These Models Compare
Selecting the right enterprise model demands more than a glance at performance charts. Organizations must weigh security architectures, compliance certifications, and integration costs to avoid fatal operational flaws.
Security and Data Handling
Security architectures have diverged significantly. Providers now adopt distinct philosophies to protect enterprise LLM assets. Because relying on post-hoc filters is no longer sufficient, this includes Anthropic’s “Constitutional AI” with a low 4.7% prompt injection rate, OpenAI’s immutable compliance logs, and Google’s confidential computing encryption.
Compliance and Regulatory Readiness
Regulated industries demand specific certifications. The choice often hinges on the deployment environment. Because general compliance is insufficient for sectors like healthcare or defense. This includes Azure’s FedRAMP High certification, Anthropic’s SOC 2 Type 2 readiness via AWS, and Gemini’s specialized tools for HIPAA-compliant healthcare workflows.
Performance and Reasoning Quality
Performance is now highly task-specific. No single model dominates every benchmark. Because specialization has replaced generalist dominance. This includes Claude’s 80.9% score in agentic coding, GPT-5.2’s perfection in abstract mathematics, and Gemini’s dominance in managing 2-million-token context windows.
Integration and Ecosystem Maturity
Infrastructure dictates the choice. Committing to a cloud ecosystem limits flexibility. Because generative AI models are now embedded components rather than standalone tools, this includes Gemini’s seamless Workspace query capabilities, OpenAI’s integration with the Microsoft control plane, and Anthropic’s platform-agnostic ties to AWS Bedrock.
So, you need an AI strategy consulting service that can help you determine if your infrastructure is mature enough to integrate generative AI models.
Cost Predictability and Scaling Behavior
Cost management requires sophistication. Simple token counting is obsolete. Because true efficiency comes from caching and predictability. This includes Anthropic’s 90% prompt caching discount, Google’s provisioned throughput units for consistent billing, and OpenAI’s focus on reducing retries through higher reasoning density.
Which Generative AI Model Is Right for Your Enterprise?
The market has matured into specific architectural niches. Generative AI models now offer distinct advantages in reasoning, safety, and context. This means aligning GPT for knowledge work, Claude for secure coding, and Gemini for massive data integration.
Mapping Models to Scenarios
Regulated Industries
OpenAI and Anthropic emerge as your primary contenders. Because data sovereignty and auditability are non-negotiable, this includes FedRAMP High certification, strict geographic data zones, and “Constitutional AI” that resists adversarial attacks.
Customer-Facing AI
High throughput and low latency are the only metrics that matter. Because customers will not wait for a slow agent, this involves deploying “Instant” models for imperceptible response times, utilizing transaction protocols for autonomous commerce, and leveraging multimodal inputs for dynamic shopping experiences. This ensures the AI Chatbot for Customer Service resolves every query in real time, reducing drop-offs, increasing repeat interactions, and improving customer retention.
Internal Copilots
The choice for internal automation depends entirely on your ecosystem because a Gemini vs OpenAI mismatch creates friction. This includes using Claude for complex refactoring, Gemini for seamless Google Workspace navigation, and GPT for high-level professional strategy.
Data-Intensive Analytics
The context window size determines your ability to process reality. Because fragmenting data destroys coherence, what this means is leveraging enterprise LLM capabilities to ingest entire codebases, analyze hours of video, and digest massive legal archives in a single prompt.
The Hybrid Strategy
A hybrid strategy is the only path to financial sanity. Because routing simple tasks to expensive models burns budget, this involves intelligent prompt routing, preserving flagship models for complex reasoning, and preventing vendor lock-in through orchestration layers.
Decision Framework
The Anthropic vs OpenAI or Google debate is solved by analyzing your primary constraints. Because every architectural choice carries a trade-off. Here is a comparison table to help you decide which LLM suits your enterprise applications.
How AQe Digital Helps Enterprises with Custom Generative AI Solutions?
The universal “best” model is a myth. Only the right architectural fit exists. Real value stems from aligning specific generative AI models with unique business objectives. This includes strict data governance, robust security requirements, and long-term strategic planning.
AQe Digital bridges the gap to production. Moving beyond simple model comparison requires a dedicated execution partner. We offer end-to-end AI development services, ensuring enterprise-grade applications for maximum ROI. So, if you are looking to leverage enterprise LLM applications, connect with our experts now.
FAQs
Anthropic, OpenAI, and Gemini differ in their model philosophy, capabilities, and enterprise focus. Anthropic emphasizes safety and controllability through its Constitutional AI approach, OpenAI focuses on high-performance general-purpose models with strong developer tooling, while Gemini is deeply integrated into Google’s ecosystem with strong multimodal and productivity use cases.
The best generative AI model for enterprise use depends on business needs. Enterprises prioritizing safety and compliance may prefer Anthropic; those seeking advanced reasoning and developer flexibility often choose OpenAI, while organizations already invested in Google Cloud and Workspace may find Gemini a better fit.
Yes, OpenAI can be used in large enterprises, including regulated industries, provided proper governance, data handling, and security controls are implemented. Many enterprises use OpenAI models through private deployments, API isolation, and additional compliance layers to meet regulatory requirements.
Yes, many enterprises adopt a multi-model strategy, using different LLMs for different workloads. For example, one model may be used for customer support, another for internal knowledge assistants, and another for code generation—helping balance risk, cost, and performance.
Enterprises should evaluate data privacy, security, compliance support, scalability, integration capabilities, cost structure, and long-term vendor roadmap. Beyond model performance, governance and operational readiness are critical factors for successful enterprise adoption.