Without active intervention, digital information inherently degrades. Customer behavior changes, file formats shift during migration, and duplicate records quietly breed in the dark corners of your servers. This invisible erosion creates a “fog of war” for decision-makers, where the dashboard might look green, but the reality on the ground is red.
This is where data quality management becomes crucial. With data quality management, enterprises can move from passive observation to active orchestration and clear the fog. Plus, the advent of AI has made data quality a necessity.
McKinsey reports that AI will help enterprises reduce total work time by 25%. However, achieving this feat will require high-quality training data. So, if you are an enterprise looking to improve data quality, this article is for you. It discusses data quality management, its dimensions, metrics, controls, and best practices.
Let’s start with the basics first.
What is Data Quality Management?
Data quality management, or DQM, is the systematic orchestration of processes, people, and technology to ensure an organization’s data is accurate, complete, and reliable. It includes practices such as data profiling, cleaning, validation, quality monitoring, and metadata management.
Successful data quality management helps you optimize datasets across dimensions such as accuracy, completeness, consistency, timeliness, uniqueness, and validity. If you are an enterprise looking to optimize data quality management, software development solutions providers can help.
These solutions providers have data practitioners who address data quality issues and help create high-quality data pipelines. DQM also functions as the tactical execution of data governance. While governance enables you to establish policies and standards, DQM enforces them. This ensures that the data remains fit for analytics, operations, and strategic decision-making.
What is the Business Impact of Data Quality?
Maintaining high-quality data in the AI era has become crucial. In fact, poor data quality costs organizations across domains $12.9 million annually. Some of the key impacts of data quality are,
- DQM Reduces Operational Drag – Data engineers and analysts often spend most of their time “firefighting” data errors. Through data quality management, you can reduce the impact of such errors.
- AI and Analytics Risks – With the widespread adoption of AI, data quality becomes essential. If your data is of low quality, the AI’s output will not meet your expectations. And that is why you must ensure data quality, especially for AI model training and analytics operations.
- Strategic Advantage – Optimal data quality management can translate into successful business initiatives. In fact, poor data quality leads to 40% of the business initiatives failing.
Why is Data Quality Management Important in 2026?
Data quality is not just about improving surface-level accuracy; it also involves assessing the data’s suitability for a user’s specific purpose and its ability to support reliable decision-making. It also helps enterprises understand how well data meets the requirements of business operations, analytics, and AI initiatives.
Here is why Data Quality Management is critical in the 2026 landscape:
1. The Foundation for Agentic AI
In 2026, the stakes for data quality are defined by the rise of Agentic AI workflows, which are projected to increase eightfold by this year. Unlike passive dashboards, AI agents actively execute tasks and make decisions based on data.
- Amplification of Error: AI systems inherit and amplify data quality issues. If the underlying data is biased, outdated, or incomplete, AI agents will “hallucinate” or execute flawed actions at high speed, turning minor data errors into widespread operational failures.
- Barrier to Adoption: Poor data quality remains the number one challenge for generative AI adoption. Nearly half of business leaders cite data accuracy concerns as the leading barrier to scaling AI initiatives from pilot to production.
2. The Necessity of “Shift Left” and Real-Time Validation
By 2026, competitive advantage is defined by an organization’s ability to “shift left” on data integrity. Traditional batch validation (checking data at the end of the day) is obsolete for modern real-time applications.
- Prevention over Cure: Organizations are moving DQM to the point of ingestion (the “left” side of the pipeline). Validating data before it enters the warehouse or lakehouse prevents “data swamps” and reduces the blast radius of errors.
- Streaming Architectures: In industries like finance and retail, data must be validated in motion (in real time). A delay in detecting a pricing error or a fraud signal can result in immediate revenue loss or compliance breaches.
3. Regulatory Compliance and Trust
In 2026, data trust is synonymous with business viability. Only a few enterprises report having the DQM processes necessary to fully trust their data, leaving the majority to make decisions based on potentially flawed information.
- Compliance: DQM is essential for adhering to strict regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Inaccurate personal data can lead to severe fines and reputational damage.
- Decision Reliability: Distorted data leads to flawed strategic decisions. Whether it is mispricing products or misallocating resources, the “garbage in, garbage out” principle is accelerated by automated analytics.
4. Transition to Automated and Autonomous Remediation
Manual data cleansing is impossible at the scale of data generated in 2026. Modern DQM relies on AI-augmented automation to handle the volume and complexity of data.
- Autonomous Healing: Advanced DQM tools now utilize autonomous AI agents to detect, diagnose, and self-heal broken pipelines without human intervention.
- Metadata Activation: Organizations are leveraging metadata to automate governance and quality checks, ensuring that data products remain reliable even as schemas and sources evolve
What are the key Data Quality Management Dimensions?
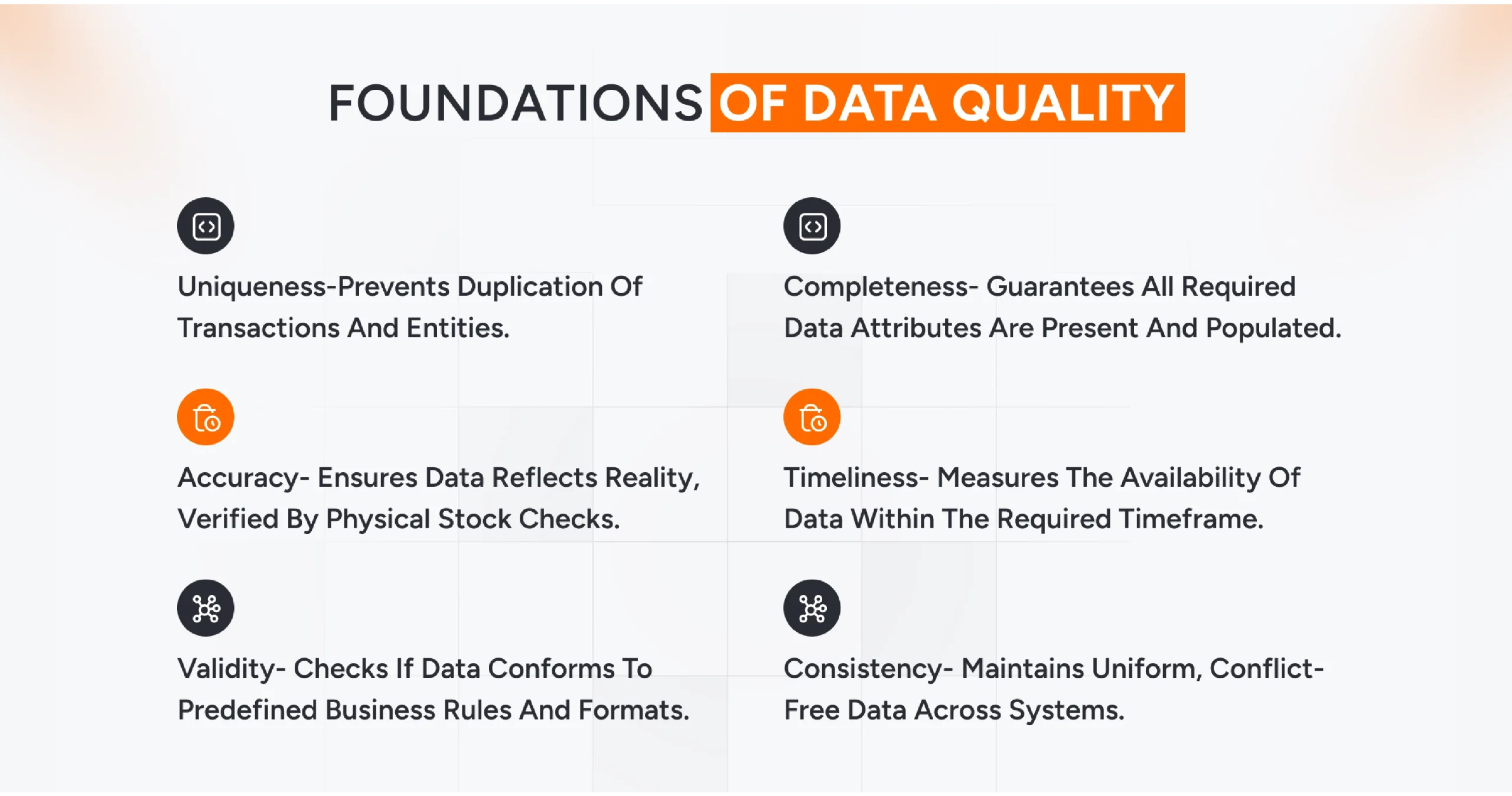
Assessing the data quality for enterprises requires focus on six core dimensions,
- Accuracy measures the degree to which data accurately reflect a real-world entity or event. It can be used to verify a recorded inventory level against physical stock.
- Data completeness is a dimension used to assess whether all the required data attributes and records are present and populated. It ensures there are no crucial gaps in the data, which can hamper the analytics solution.
- Data consistency ensures that values remain uniform and free of conflicts across systems. This ensures that customers’ data across CRM and billing systems, for example, is the same.
- Data timeliness refers to the time lag between an event and its availability for use. This measures whether the data is accessible within the timeframe required to be valuable.
- Data validity is a metric that helps enterprises check if data conforms to predefined business rules, formats, and constraints.
- The uniqueness of the data ensures that no transaction or entity is recorded more than once, preventing duplication.
All of the above dimensions enable enterprises to ensure not only data availability but also data trust.
What is Data Quality vs. Data Availability?
What is data quality? It is often confused with simple availability. While data availability ensures that information is accessible and retrievable when needed, it alone does not guarantee utility.
Successful data quality control helps you distinguish between data that is merely delivered instantly and data that is actually trustworthy. Accessible data has no value if it is not timely or accurate. For instance, data might be delivered instantly (high availability) but represent a state from three years ago (low currency). If you are an enterprise looking to optimize software data quality, focusing on trust rather than just speed is essential.
This ensures that the data remains fit for compliance, governance, and reliable decision-making.
What is a Data Quality Management Framework?
A Data Quality Management Framework is the orchestration of processes, policies, and tools to consistently monitor data quality and ensure data is consistent with organizational needs. It includes practices such as data profiling, data cleansing, data monitoring, and master data management.
Successful implementation of a data quality framework helps you optimize datasets across dimensions such as structure, accuracy, and reliability. If you are an enterprise looking to optimize your data quality management, specialized solution providers can help.
These solutions use specialized tools to determine which quality measures to apply and identify areas that require improvement. This ensures that the data remains fit for compliance, security, and strategic decision-making.
What are the Core Components of a DQM Framework?
Maintaining trusted data requires more than just ad-hoc fixes. In fact, a robust framework serves as the backbone for ensuring data accuracy and consistency. Some of the key components of data quality control are,
- Data Profiling involves scrutinizing your existing data to understand its structure and identify anomalies. It uses data profiling techniques to detect irregularities. This ensures you know the baseline health of your data before attempting to fix it.
- Data Cleansing and validation involve correcting or removing detected errors to improve accuracy and reliability. Various methods, such as machine learning algorithms, rule-based systems, and manual curation, are employed here. This ensures that the data meets software data quality requirements.
- Data Monitoring is the continuous process of ensuring the long-term consistency of your data. Advanced data quality monitoring systems can detect anomalies in real time and trigger alerts for further investigation.
- Data Governance involves creating policies, assigning roles, and monitoring compliance. Well-defined policies guide how data should be collected, stored, and accessed. This ensures that data is handled securely and meets data quality standards.
- Master Data Management (MDM) is a set of best practices for data integration and data quality. Effective MDM consists of consolidating data from multiple sources to provide a unified, accurate representation of key data entities.
What are the Steps for Data Quality Implementation?
Implementing high-quality data processes in a complex environment has become crucial. In fact, a lack of structured implementation leads to “operational drag” and failed initiatives. Some of the key best practices for data quality control are,
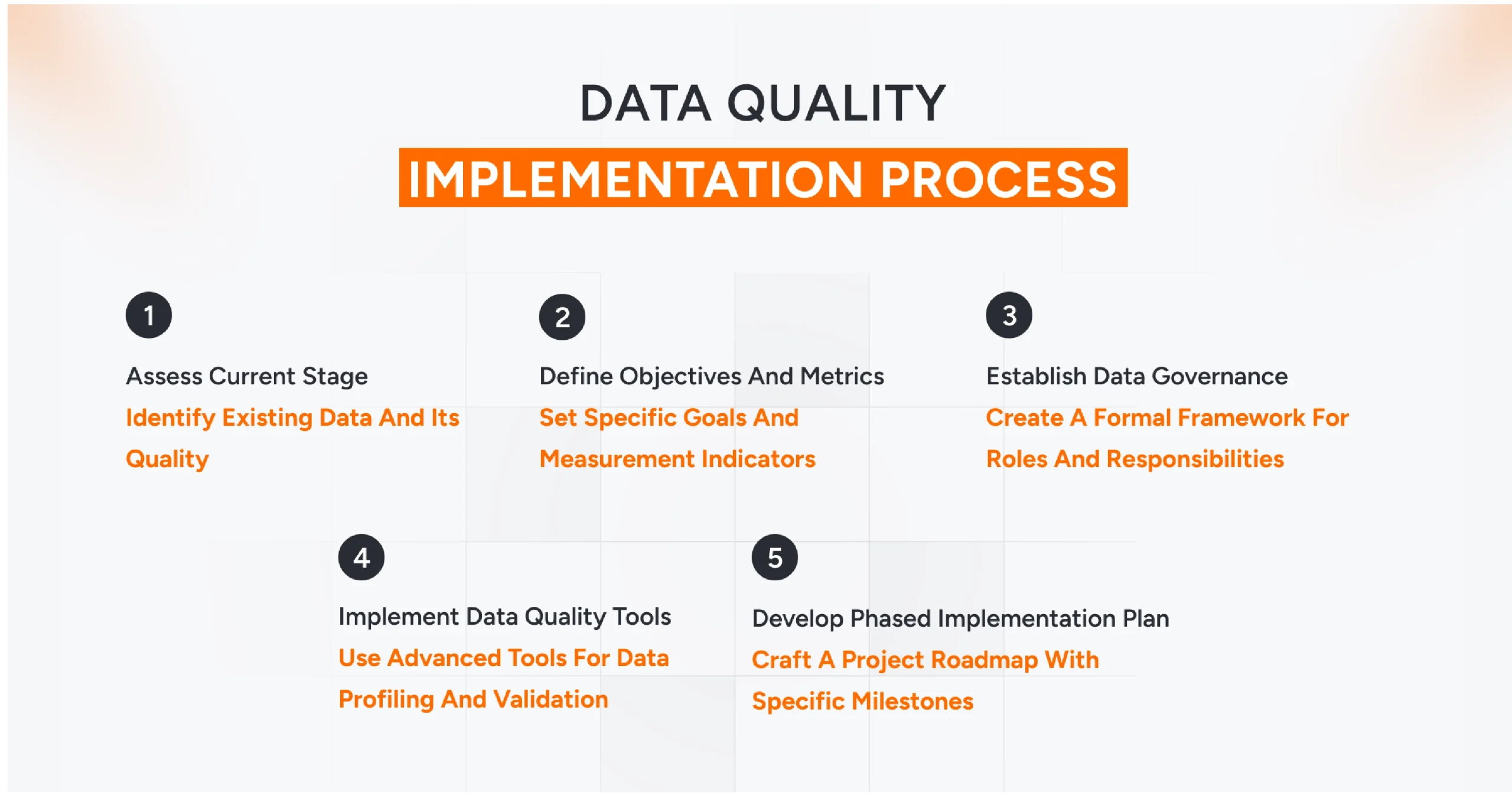
- Assess Current Stage- Identify what data exists, where it’s stored, and its current quality. Reviewing existing tools and workflows helps you understand the baseline before applying data quality best practices.
- Define Objectives and Metrics- Define specific goals for improvement and determine how they align with ROI. This is where you decide how to measure data quality effectively using tangible indicators.
- Establish Data Governance- Create a formal framework that outlines roles and responsibilities. This identifies stakeholders accountable for specific data quality standards, ensuring that management is not just an IT function but a business mandate.
- Implement Data Quality Tools- Use advanced tools that automate data profiling, cleansing, and validation. Investing in these solutions ensures that data validation rules are applied consistently at scale.
- Develop a Phased Implementation Plan- Craft a project roadmap with specific milestones. This ensures that each phase focuses on specific objectives, much as data cleansing targets the issues identified during profiling.
What are Data Quality Management Best Practices?
Data quality best practices serve as the systematic orchestration of governance, automation, and “shift-left” strategies to ensure an organization’s data assets are trusted, scalable, and compliant. This framework includes practices such as data quality checks, data profiles, validation rules, and automated data quality monitoring.
Successful data quality management helps you optimize pipelines across data quality dimensions such as accuracy, completeness, and timeliness. If you are an enterprise looking to optimize software data quality, automated observability solutions can help.
These solutions enable you to move from reactive “cleanup” to proactive prevention. This ensures data accuracy and consistency for analytics and AI, making data truly fit for purpose.
Some of the data quality management best practices are,
Agentic Data Remediation
By 2026, data quality management is shifting from manual, reactive fixes to autonomous, agentic workflows.
- Beyond Passive Monitoring: Agentic AI workflows are projected to increase eightfold by 2026. These systems move beyond simple dashboards to actively detect, diagnose, and self-heal data issues.
- Automated Correction: Modern tools are adopting “shift left” strategies that leverage AI to automate remediation tasks, such as deduplication, format standardization, and rule generation, without human overhead. This capability is critical because AI agents amplify data quality issues; if the underlying data is flawed, agentic systems will inherit errors and spread them at scale.
- Operational Efficiency: By automating the “firefighting” of data errors, agentic remediation significantly reduces the operational drag.
Data Contracts Adoption
Data contracts are emerging as a vital mechanism for formalizing and enforcing data standards between data creators (producers) and data users (consumers).
Alignment at the Source: Data contracts define the structure, format, quality standards, and usage rights of the data. They ensure data quality is enforced before ingestion, preventing the “garbage in, garbage out” cycle.
- Prevention of Downstream Breakage: By enforcing these contracts, organizations prevent issues caused by unexpected upstream changes, such as schema drift, ensuring that data products remain reliable and usable.
- Implementation: These contracts are often established during the data product design phase, formalized through metadata activation, and integrated into deployment pipelines to act as gatekeepers for data integrity.
Synthetic Data Verification and AI Readiness
As the adoption of Generative AI accelerates, validating the data used to train and ground these models has become a critical quality check.
- Validating AI Inputs: With data quality and governance identified as the top challenges for Generative AI adoption, organizations must ensure datasets are free from bias and inaccuracies to prevent AI “hallucinations.”
- Synthetic Data Utility: Organizations are increasingly leveraging synthetic data to train AI models and process analytics, particularly to protect data privacy and secure sensitive identifiers.
- Statistical Fidelity: To ensure these AI systems function correctly, data teams must verify that training data, whether real or synthetic, maintains high integrity. Poor quality data in this context leads to model drift and unreliable predictions, making the validation of these datasets a prerequisite for AI success.
What are Data Quality Standards and Controls?
Maintaining trusted data in a complex digital landscape has become crucial. In fact, reactive firefighting costs organizations millions in “operational drag.” To mitigate this, enterprises must enforce robust data quality standards. Some of the key components of data quality control are,
- Shift-Left Data Quality- The most effective way to reduce costs is to validate data at the source. By implementing data validation rules at API endpoints or web forms, you prevent errors from entering the data quality framework.
- Embed Quality Checks in Pipelines- Modern architectures require data quality checks to be “baked in.” Using automated data quality monitoring ensures that invalid data is routed to quarantine tables rather than polluting the data warehouse.
- Observability vs. Monitoring- Understanding data observability vs data quality is essential. While monitoring tracks metrics, observability provides end-to-end visibility, allowing you to detect anomalies before they impact downstream dashboards.
How AQe Digital Ensures Optimal DQM for Your Enterprise?
Data Quality Management at AQe Digital is not just about fixing errors; it’s about transforming your raw data into a strategic asset. We go beyond reactive cleanup to establish a resilient, AI-ready data foundation through advanced data analytics and engineering solutions.
Successful data quality initiatives help you optimize business intelligence across dimensions such as compliance, scalability, and trust. If you are an enterprise looking to optimize your data quality management strategy, AQe Digital can help.
Our experts utilize advanced data profiling techniques and governance frameworks to address data quality issues at the source. This ensures that your organization moves from “firefighting” insufficient data to leveraging it for competitive advantage.
FAQs
The six core dimensions are accuracy, completeness, consistency, timeliness, validity, and uniqueness. Together, these metrics ensure that data is not only available but also trustworthy and fit for strategic decision-making.
High-quality data is essential because AI agents inherit and amplify errors found in biased or incomplete datasets. Without accurate inputs, Agentic AI workflows can "hallucinate" and execute flawed actions at scale, leading to operational failures.
"Shift Left" involves moving data validation to the point of ingestion, the beginning of the pipeline, rather than checking it downstream. This proactive strategy prevents "data swamps" and reduces the high cost of fixing errors after they have entered the warehouse.
Data availability ensures that information is accessible and retrievable when needed, whereas data quality guarantees that it is accurate, timely, and reliable. Accessible data is of little value to an enterprise if it represents an outdated or incorrect state.
A robust DQM framework orchestrates data profiling, cleansing, validation, monitoring, and governance. These components work together to detect anomalies, enforce standards, and ensure data remains consistent with organizational needs and compliance regulations.