The cloud has emerged as a transformative force for enterprises to operate and manage data providing access to servers, networks, storage, development tools, and applications via the Internet.
Cloud computing enables businesses to have unparalleled scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and operational efficiency aligning technology infrastructure with evolving business needs and innovation. Also, it helps businesses with disaster recovery, business continuity, security, global accessibility, speed at market, integration, and enhanced collaboration.
Sighting the current digital landscape, the majority of businesses around the globe have migrated most of their IT environments to the cloud and many are in the process of doing so. Enterprises are undergoing cloud migration eliminating traditional on-premise infrastructure for significant cost-savings and harnessing the potential of their Accuracy, fostering agility and resilience in an increasingly data-driven world.
Cloud storage and processing capabilities, combined with the power of cloud analytics, ensure that data is readily accessible, secure, and scalable. This has driven the majority of businesses around the globe to adopt cloud migration. From streamlining operations to enhancing data accessibility, cloud migration offers limitless advantages, positioning businesses for sustained growth in an evolving digital landscape.
Why Are Enterprises Opting For Cloud Migration?
Flexibility, scalability, cost-effectiveness, and strategic data management are the major factors for enterprises to look forward to cloud migration.
Businesses want to eliminate outdated and inefficient legacy infrastructure, such as hefty servers, potentially unreliable firewall appliances, and infrastructure management, or abandon hardware or software that is not operating at full capacity.
The cloud offers agility and optimized security, making it the topmost priority for enterprises that want to deal efficiently with fluctuating demands without the heavy logistical burdens of physical infrastructure. The cloud supports secured remote data accessibility and applications, making it more convenient for businesses to operate from multiple locations.
Additionally, businesses can drive innovation, collaboration, and operational efficiency as the cloud supports the adoption of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT). It provides businesses with tools to create new revenue streams, optimize operations, identify opportunities, and have easy-to-manage IT infrastructure with minimized cost.
Advantages Of Cloud Migration
The benefits of cloud migration are immense and wide-ranging, making it a transformative strategy for businesses. Here are some of the key advantages:
Cost Efficiency
The predominant reason for businesses to migrate to the cloud is to minimize the IT infrastructure management cost while improving data accuracy. Companies with traditional data centers must invest heavily in hardware, infrastructure, maintenance, and utilities. For companies with fluctuating workloads, the cloud is the best option for substantial savings, as they only pay for the resources they use and can eliminate the cost of licensing fees for third-party apps.
Scalability and Flexibility
Businesses can quickly scale their resources up or down in response to changing market demands with the cloud. For example, for seasonal increased visitors, an eCommerce platform might need additional cloud resources. With the cloud, it is possible to add or remove resources quickly without physical upgrades or downtime. For businesses aiming to expand or adjust quickly to new requirements, scalability and flexibility become the key factors.
Disaster Recovery
With automated backups, real-time data replication, and disaster recovery solutions cloud helps businesses have uninterrupted workflows. All these features help business operations keep going even during system failures or natural disasters ensuring data security. Cloud helps significantly reduce downtime and the risk of data loss with robust data recovery options, including multi-location backups.

Download the Ultimate Guide for Cloud Migration
Send download link to:
Enhanced Collaboration and Productivity
Cloud technologies enable better collaboration allowing users to access and work on documents and applications simultaneously from anywhere, improving efficiency and reducing delays. With real-time updates and better communication channels, cloud technologies foster better collaboration in distributed teams and support a seamless workflow.
Innovation and Competitive Advantage
Cloud migration helps businesses innovate and stay competitive with access to next-gen technologies such as AI, machine learning, and big data analytics. Cloud platforms support the rapid development and deployment of new applications, products, and services, allowing businesses to respond quickly to market changes and technological trends.
Let’s understand the cloud migration process we undertake to deliver result-oriented solutions.
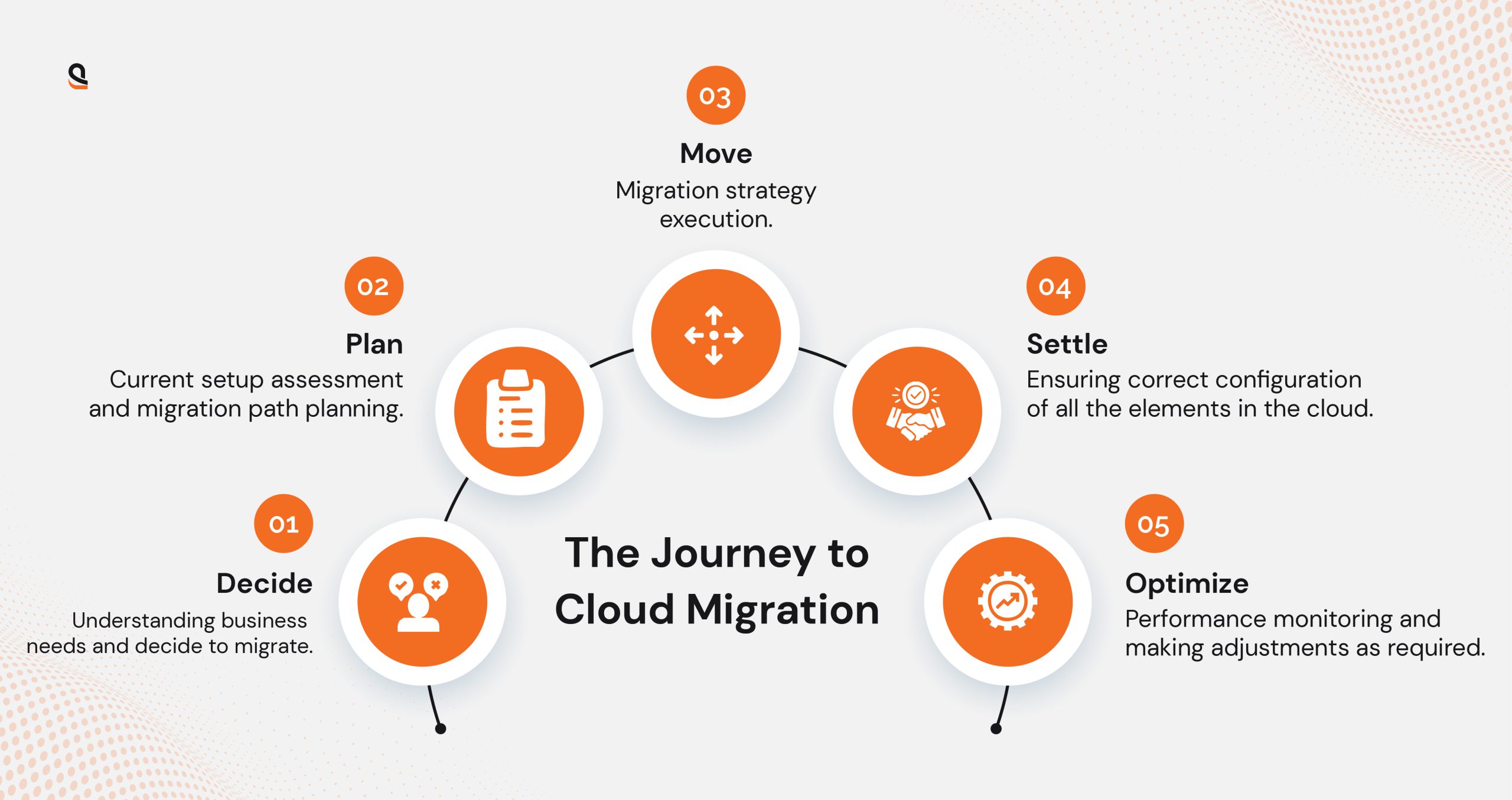
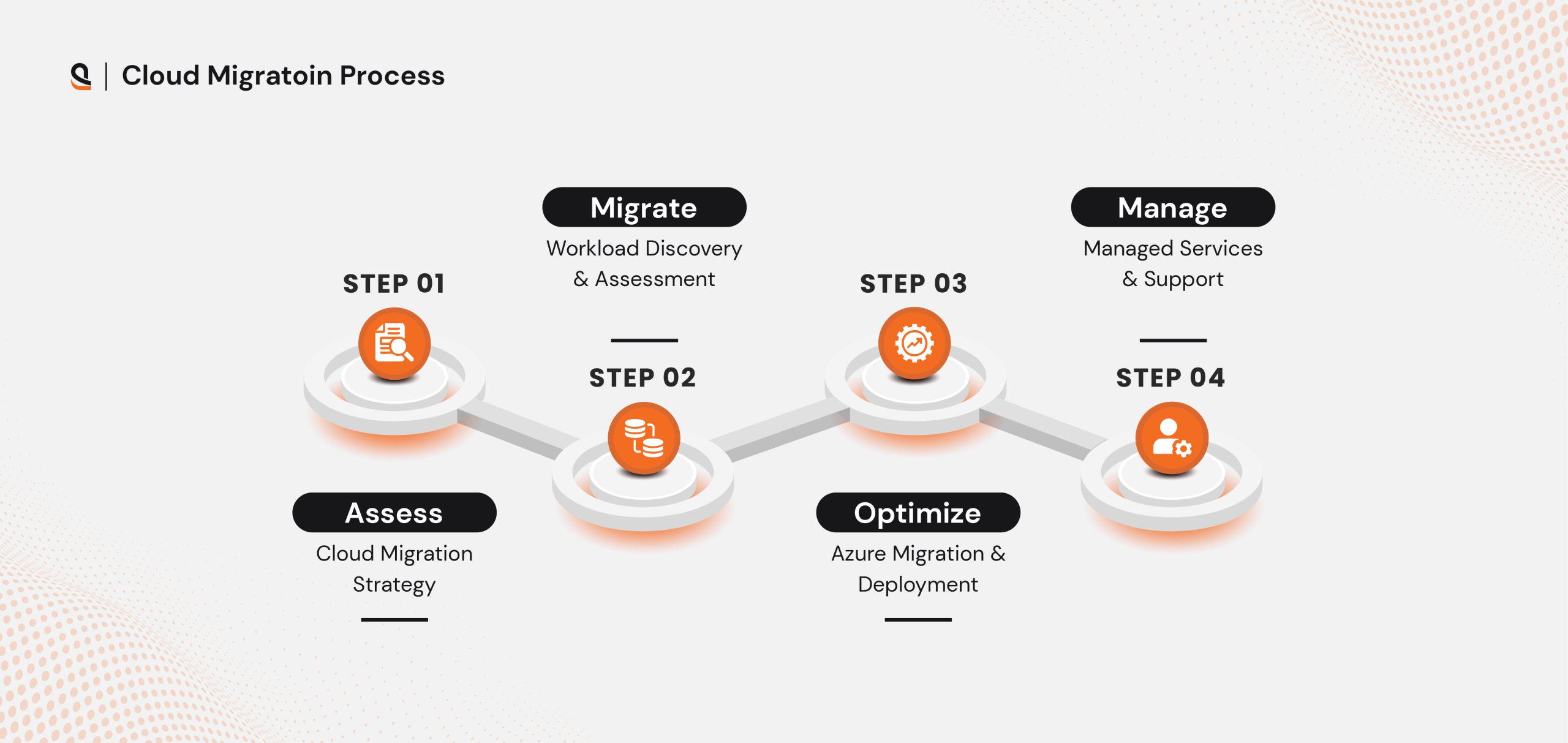
Our Cloud Migration Process
To leverage all the advantages of cloud migration- it is important to have a well-planned, strategic, and goal-oriented cloud migration process. However, the cloud migration process and strategy are subjective to many aspects like business requirements, goals, challenges, and the existing IT infrastructure. Here is our cloud migration process:
Assess
Our assessment for cloud migration involves three essential steps: Discovery & Assessment, Planning, and Preparation. During the discovery and assessment stage, our team works on multiple fronts such as gathering relevant information and evaluating resource readiness and business operations. We also work on estimating costs and complexities along with document findings. The planning phase helps us set clear goals and current environment assessments.
After analyzing all the aspects, the right migration strategy is chosen, timelines and budgets are developed, and risks are mitigated. In the Preparation phase, we verify workloads for compatibility, configure resources and security, and conduct pre-migration testing for migration plan validation addressing potential issues.
Key considerations for this stage:
- Identify on-premises resources for migration.
- Gather detailed information about each resource.
- Evaluate readiness and compatibility with the cloud platform.
- Estimate migration costs and complexities.
- Document findings and develop a detailed migration plan.
- Set clear goals and objectives for the migration.
- Assess the current environment and choose a migration strategy.
- Develop a timeline and budget.
- Configure cloud platform resources, networks, and security.
- Conduct pre-migration testing to validate the plan and resolve issues.
Migrate
The Migration phase involves transferring on-premises workloads to the cloud, marking the culmination of the assessment and planning stages. This step requires executing the chosen migration strategy, closely monitoring the migration process to promptly address any challenges, and ensuring that applications function properly in the respective cloud’s environment.
Key points to consider for migration:
- Execute the migration strategy using the chosen method.
- Monitor the migration process to identify and address issues promptly.
- Verify that applications are functioning correctly in the cloud’s environment.
Optimize
The Optimize phase includes Validation and Optimization steps to ensure a smooth and efficient migration outcome. In the Validation step, the migration plan and workloads are extensively tested in a staging environment to confirm functionality, validate security measures for compliance, and document the migration process and results. Once validated, the Optimization step focuses on enhancing resource performance and cost efficiency by adjusting settings for scalability, leveraging platform-native services, and implementing continuous monitoring and optimization to maintain performance and address any post-migration issues.
The entire Optimization includes:
- Test migration of workloads in a staging environment to ensure functionality.
- Validation of security measures and compliance requirements.
- Documentation of the migration process and results.
- Adjustment of resource settings for performance and scalability.
- Leveraging cloud-native services for better functionality and cost efficiency.
- Continuous monitoring and optimization to maintain performance and address issues.
Manage
The Manage phase, which includes Post-Migration, focuses on ensuring the migrated workloads operate smoothly in the cloud’s environment. This step involves continuous monitoring, training operations personnel on the new environment, and documenting configurations and best practices. Once all systems are verified to be functioning correctly, the old environment can be decommissioned.
- Monitor workloads continuously to ensure proper functionality.
- Train operations personnel on managing the new cloud environment.
- Document configurations and best practices for future reference.
- Decommission the old environment once the migration is validated.
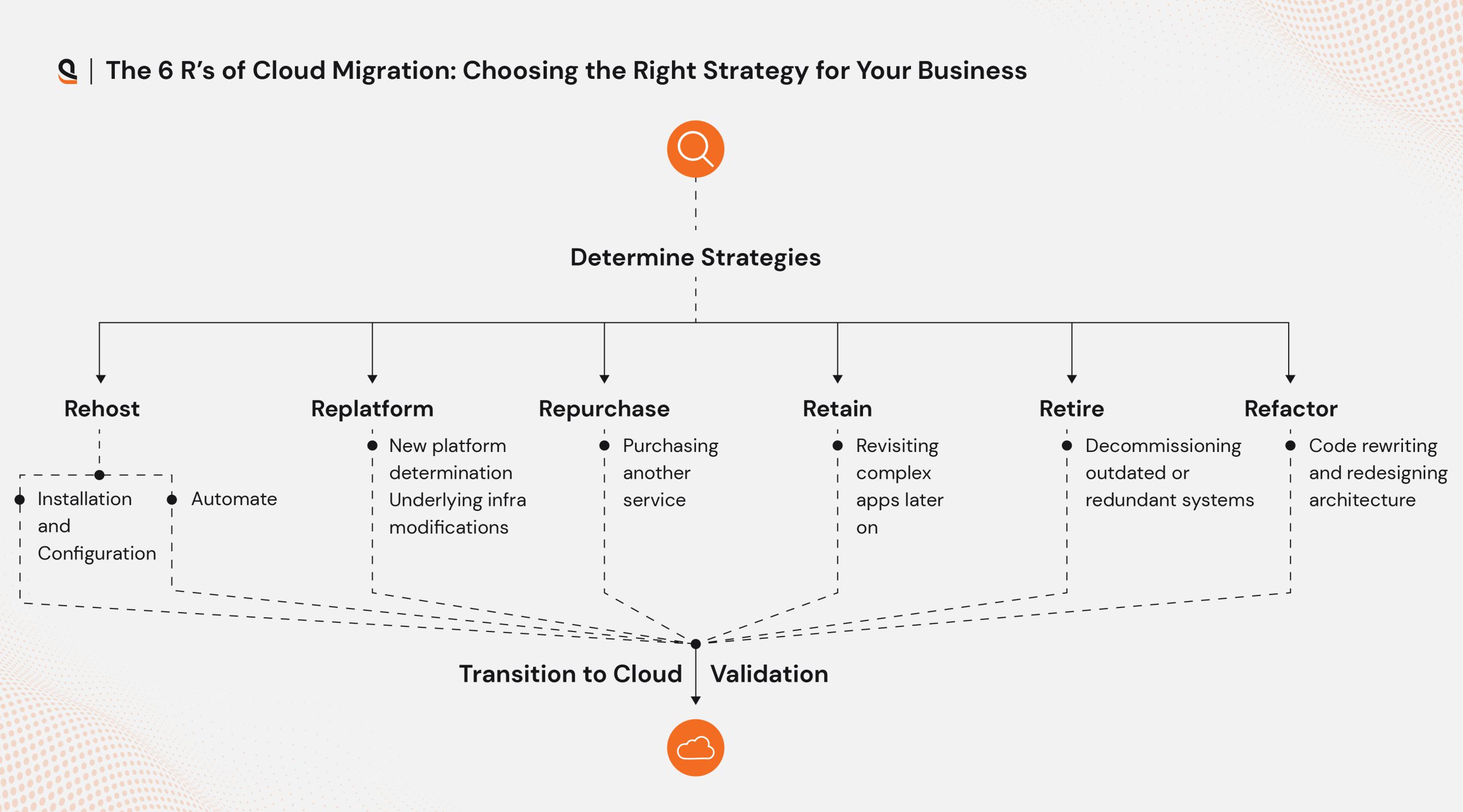
The 6 R’s of Cloud Migration: Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Business
For organizations looking for scalability, innovation, and streamlining their IT infrastructure cloud migration is a better option. Every organization has different objectives, challenges, existing infrastructure, budget, and technical capabilities. To address these multi-factorial requirements there are different migration strategies widely known as “6 R’s of Cloud Migration”. Here’s a breakdown of each strategy to help you better understand it.
- Re-Host
Widely known as “Lift and Shift,” with the Re-host strategy businesses can move their current on-premise environment to the cloud with minimal changes. This approach doesn’t require extensive reconfigurations or architectural changes making it widely popular. It is like creating an exact copy of your existing infrastructure and making it host on the cloud platform.This strategy is cost-effective and quick to implement, ideal for businesses new to cloud migration and want to have an on-premise setup on the cloud. It offers limited optimization benefits but can be a solid starting point for organizations exploring cloud adoption. - Re-platform
Re-platforming is similar to the Re-host strategy but involves making small adjustments to optimize your applications for better performance in the cloud. These changes might include updating operating systems, databases, or middleware to take advantage of cloud-native features.This approach requires technical expertise, as some programming and reconfiguration may be necessary. Businesses that want to test the cloud’s potential for performance improvement and cost savings without diving into a full overhaul of their applications often choose Re-platforming. It strikes a balance between simplicity and optimization. - Repurchase
The Repurchase strategy involves replacing your current environment with a new, cloud-native product. For instance, businesses can move from an outdated legacy CRM to an advanced Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solution like Salesforce.Alternatively, organizations can move existing software licenses from on-premise servers to cloud-based servers allowing them to phase out legacy systems and adopt cost-effective, modern cloud solutions. - Retain
Migration of certain data or applications is not possible due to compliance or technical constraints. In such scenarios, retention of the current environment is the most suitable option. For an organization having highly sensitive data, it is better to remain on-premise for regulatory reasons.Organizations can keep some workloads on-premise and move others to the cloud by adopting a hybrid model. With this flexible approach, organizations can meet their specific operational requirements while migrating at their own pace. - Retire
During the cloud migration process, it is important to evaluate the existing IT infrastructure- its efficiency and relevance. It is crucial to evaluate the applications and services that are no longer valuable. The retire strategy involves decommissioning outdated or redundant systems instead of migrating them to the cloud.This helps streamline your IT environment, reduce costs, and free up resources for more critical operations. - Refactor
Refactoring, or re-architecting, is a complex approach that is the most labor-intensive strategy. This approach requires significant time and resources as it involves redesigning and rebuilding applications from scratch to be fully cloud-environment compatible.It offers the greatest long-term benefits, including enhanced scalability, compatibility with future cloud technologies, and the ability to align with evolving business needs and scale.
Different Types Of Cloud Migrations
- Private to Public Cloud Migration: Ideal for organizations looking for cost savings, scalability, and flexibility.
- Hybrid Cloud Migration: Combination of the private cloud’s security with the scalability of the public cloud.
- Multi-Cloud Migration: Eliminate vendor lock-in, and optimize performance and cost by utilizing multiple cloud providers.
What Care Needs to Be Taken During Cloud Migration?
While cloud migration offers a host of benefits, it also involves certain risks and challenges that must be addressed to ensure a smooth transition.
Assessment of Current Infrastructure
- Assess the existing infrastructure to determine cloud suitability for workloads.
- Identify workloads to be re-platformed, refactored, or kept on-premises.
- Analyze the potential impact of migration to set clear expectations.
Data Security and Compliance
- Ensure sensitive data is encrypted during migration.
- Verify data security and privacy measures in the cloud environment.
- Address compliance requirements, especially in regulated industries.
- Confirm the cloud provider adheres to relevant regulations and standards.
Selecting the Right Cloud Provider
- Evaluate cloud providers based on pricing, services, and support.
- Consider the geographical location of data centers for compliance and performance.
- Assess the provider’s reliability, reputation, and service flexibility.
Cost Management and Optimization
- Monitor cloud usage to prevent unexpected costs.
- Use cost management tools to optimize resource allocation.
- Avoid over-provisioning by tracking and analyzing resource consumption.
Training and Change Management
- Train employees on new cloud tools, workflows, and best practices.
- Communicate clearly about the changes and their benefits.
- Implement change management strategies to guide the transition process.
Conclusion
Cloud migration is not just a mere technical process, it is a strategic move to drive efficiency, innovation, cost-effectiveness, and growth for the organization. With the right strategy and approach, businesses can meet their objectives, requirements, and challenges with cloud migration.
AQe Digital can help you have a seamless cloud migration journey to make your business agile, flexible, and streamlined with secured data management. Our cloud experts leverage the latest technologies, tools, and practices capitalizing on the power of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Data Analytics to deliver end-to-end cloud services.